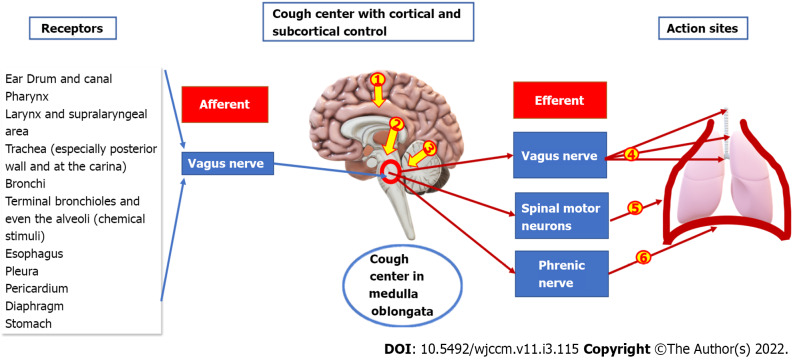
Figure 1.
Cough reflex. The cough center lies in the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. Cough receptors project through the vagus nerve to relay neurons in the solitary nucleus, which project to other parts of the respiratory network, especially the pre-Bötzinger complex. Higher brain centers (cerebral cortex[1]) provide voluntary control over cough, e.g., cough inhibition. However, voluntary coughing does not seem to activate medullary systems. Subcortical centers[2] receive signals from other receptors and other emotional stimuli acting through the hypothalamus. Cerebellum[3] also has control over the cough center. The cough center starts the cough by signaling to the effector organs through the vagus nerve to the larynx, trachea, and bronchi[4], spinal motor neurons[5] to the expiratory muscles, and the phrenic nerve[6] to the diaphragm.