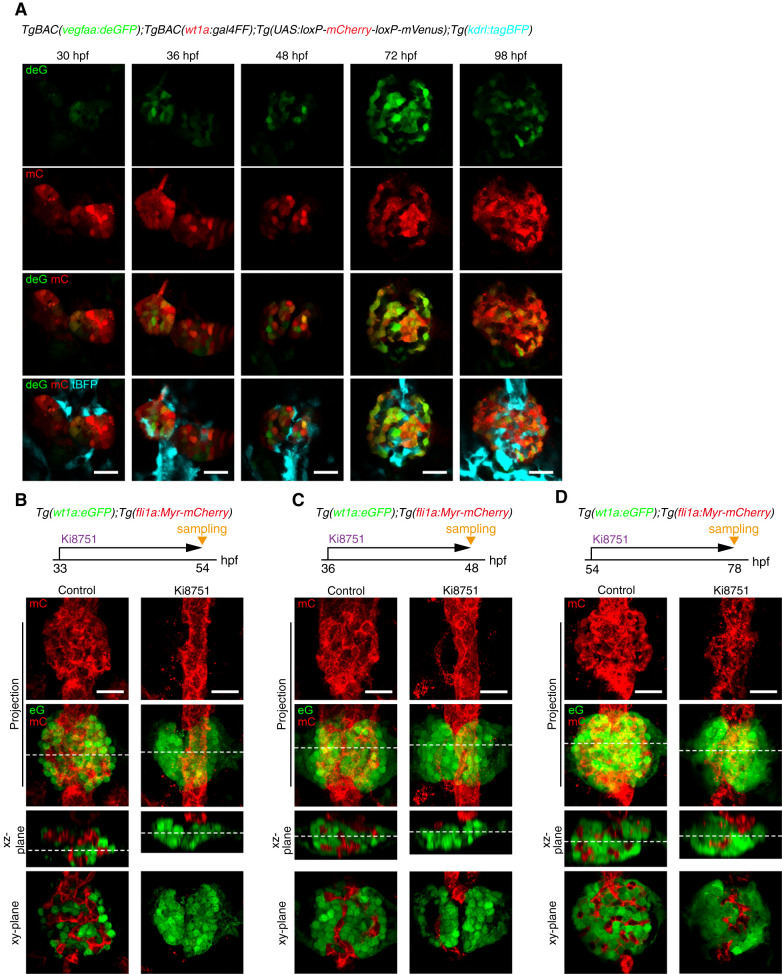
Figure 2.
Requirement of Vegf signaling for glomerular capillary formation. (A) Confocal single z-plane images of pronephric glomeruli in TgBAC(vegfaa:deGFP);TgBAC(wt1a:gal4FF);Tg(UAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-mVenus);Tg(kdrl:tagBFP) embryos and larvae at the stage indicated at the top of each column. Ventral view images of the fixed embryos and larvae were acquired as shown in Figure 1A. Ventral views; anterior to the top. First row, vegfaa:deGFP fluorescence (deG; green); second row, wt1a:gal4FF;UAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-mVenus fluorescence (mC, red); third row, the merged images of deG and mC fluorescence; fourth row, the merged images of deG, mC, and kdrl:tagBFP (tBFP, cyan). Scale bars; 20 μm. (B–D) Effects of Ki8751, a Vegf receptor inhibitor, on glomerular capillary formation. Confocal fluorescence images of the pronephric glomeruli in Tg(wt1a:eGFP);Tg(fli1a:Myr-mCherry) zebrafish treated with DMSO (control) or with 1 μM Ki8751 from 33 to 54 hpf (B), from 36 to 48 hpf (C), and from 54 to 78 hpf (D). The z-projection and single-plane images are shown as Figure 1B. Scale bars; 20 μm. Vegf, vascular endothelial growth factor; deGFP, destabilized enhanced green fluorescent protein; hpf, hours post fertilization.