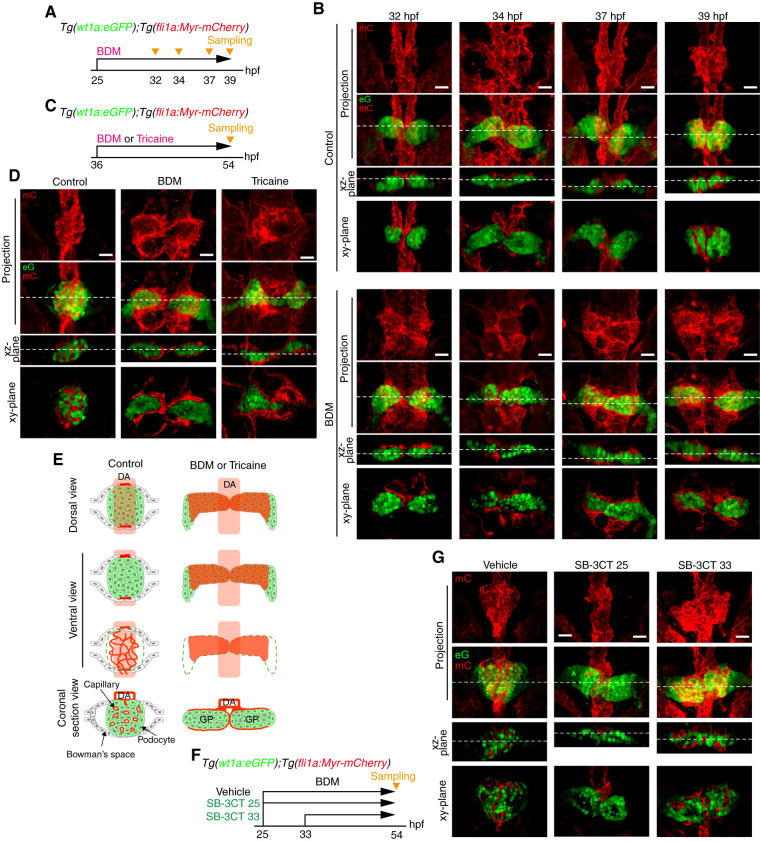
Figure 4.
Requirement of blood flow for glomerular capillary formation. (A–E) Effects of stopping blood flow on glomerular capillary formation. (A and B) Tg(wt1a:eGFP);Tg(fli1a:Myr-mCherry) embryos were treated with vehicle (upper panel in B) or BDM (lower panel in B) from 25 hpf and fixed with paraformaldehyde at 32, 34, 37, and 39 hpf. Subsequently, the fixed embryos were imaged with a confocal upright microscope as shown in Figure 1A. (B) The z-projection and single-plane images of the pronephric glomeruli at the stages indicated at the top are shown as in Figure 1B. Scale bars: 20 μm. (C and D) Tg(wt1a:eGFP);Tg(fli1a:Myr-mCherry) embryos were treated with vehicle (control), BDM, or tricaine from 36 hpf, fixed at 54 hpf, and imaged with a confocal upright microscope as shown in Figure 1A. (D) The z-projection and single-plane images of the pronephric glomeruli are shown as in Figure 1B. Scale bars: 20 μm. (E) Schematic illustration of the pronephric glomeruli in embryos treated with vehicle (control) or with BDM or tricaine as observed in (D)are shown as in Figure 1C. (F and G) Effects of SB-3CT, an inhibitor for MMP2 and MMP9, on glomerular capillary formation. Tg(wt1a:eGFP);Tg(fli1a:Myr-mCherry) embryos were treated with vehicle from 25 hpf (control) or with SB-3CT from 25 (SB-3CT 25) or 33 hpf (SB-3CT 33), fixed at 54 hpf, and imaged with a confocal upright microscope as shown in Figure 1A. The z-projection and single-plane images of the pronephric glomeruli are shown as in Figure 1B. Scale bars: 20 μm. BDM, 2,3-butanedione monoxime.