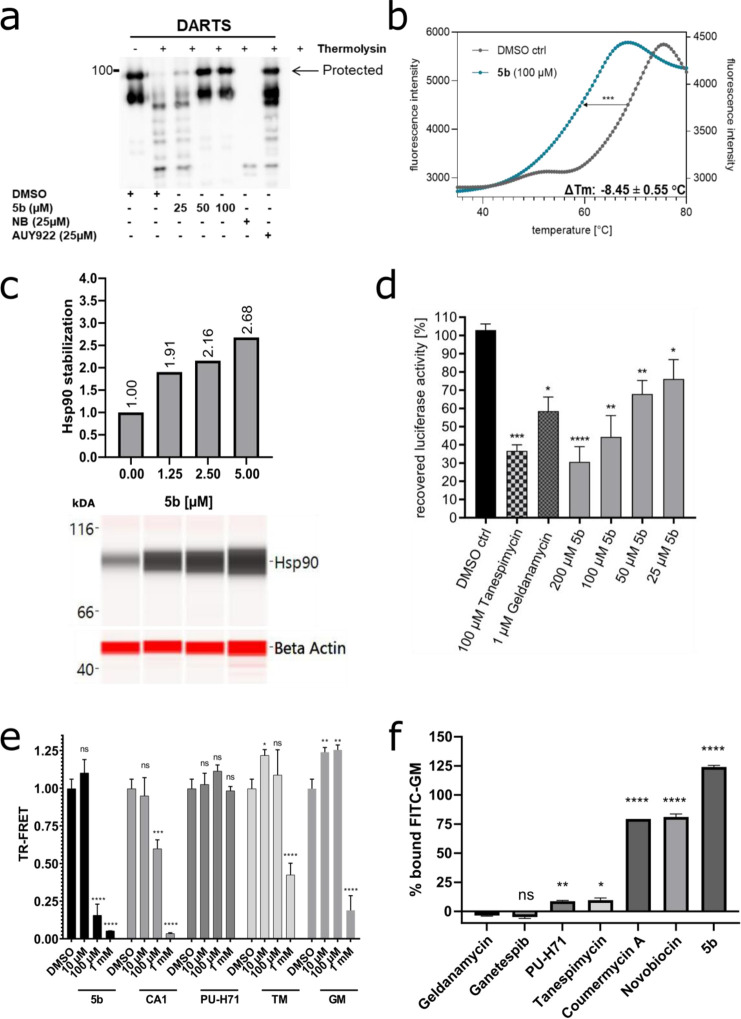
Figure 3.
Specificity of 5b against Hsp90 CTD and its cochaperone function. (a) Recombinant (full-length) Hsp90α (1 μg) was incubated with 5b at indicated concentrations, followed by digestion with thermolysin. Treated protein samples were electrophoresed (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotted with anti-Hsp90α for detecting the protection of Hsp90α protein by 5b (the upper band is protected from proteolysis). (b) A cell-free thermal shift assay was performed by incubating recombinant Hsp90α CTD protein with 5b at an increasing temperature (up to 95 °C). The melting temperature (Tm) without inhibitors (DMSO) was used as a control. (c) Dose-dependent intracellular (K562 cells) thermal stabilization (CETSAITDRF) of Hsp90 after 5b incubation (24 h) at its increasing concentration (1.25–5 μM). (d) 5b inhibits the Hsp90α chaperone function, comparable to TM and GM, in the cell-free luciferase refolding assay, where the incubation of the inhibitors prevented the rabbit reticulocyte lysate (a source of Hsp90)-assisted refolding of denatured luciferase. (e) Incubation of 5b blocked the binding of Hsp90 CTD-interacting cochaperone (PPID) in TR-FRET measurements. (f) 5b did not reduce the amount of Hsp90-bound FITC-labeled GM and, therefore, does not compete for the GM binding pocket of full-length Hsp90α. Unlabeled GM, GP, PUH71, and TM served as positive controls and NB and CA1 as negative controls.