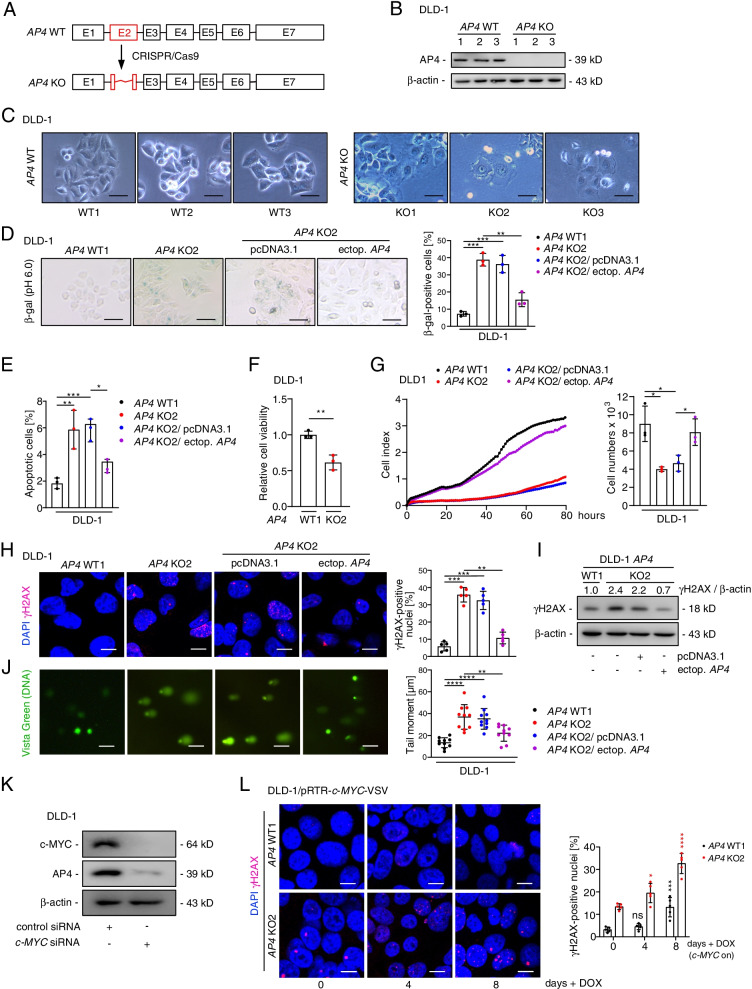
Fig. 1.
AP4 inactivation induces DNA damage and senescence in CRC cells. A Scheme of targeting exon 2 (shown in red) of TFAP4/AP4 using CRISPR/Cas9. B AP4 detection by Western blot analysis. β-actin served as a loading control. C Phase contrast images of untreated cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. D Detection of senescent cells using pH 6 β-gal staining 48 h after transfection. Ectopic expression of AP4 was achieved using a pcDNA-AP4-VSV vector described in [4]. Three fields of 120 cells in total were evaluated. Scale bars: 100 μm. E Quantification of apoptotic cells by Annexin V detection 48 h after transfection. F MTT assay results obtained 72 h after seeding. G Proliferation was determined by impedance measurement in E-plates 48 h after transfection in the indicated cells (left panel). Cell numbers were determined at the last time point (right panel). H Detection of γH2AX foci 48 h after transfection. Quantification of 5 fields with 150 cells in total. Scale bars: 20 μm. I Western blot analysis 48 h after transfection. J Comet assay 48 h after transfection. Quantification of DNA tail moment in 10 fields with 150 cells in total. Scale bars: 10 μm. K Western blot analysis after 48 h after c-MYC siRNA transfection. L γH2AX foci detection after c-MYC induction by addition of DOX. Quantification of 5 fields with 150 cells in total. Scale bars: 20 μm. Results are presented as the mean + SD with (n = 3) for D-G, (n=5) for H+L and (n=10) for J with *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001