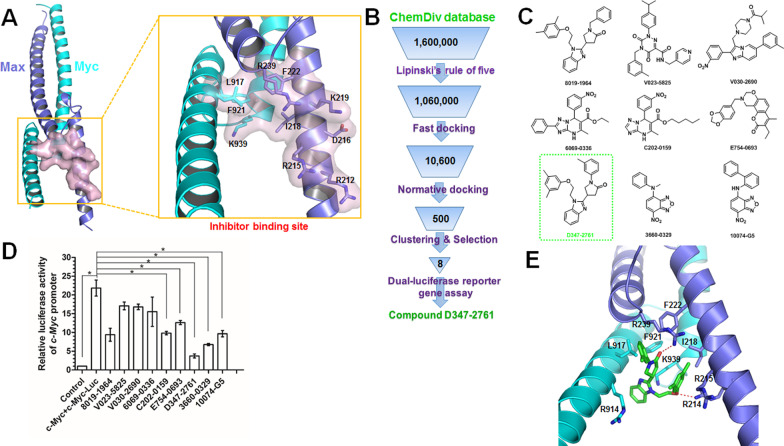
Fig. 1.
Molecular docking-based virtual screening for c-Myc inhibitors. A Crystal structure of c-Myc/Max complex and the well-defined inhibitor binding site formed by the interface of c-Myc/Max. Ten key residues attributed to the forming of the binding site were labeled. The proteins c-Myc and Max were shown in cartoon models and colored in cyan and blue, respectively. B Workflow of the molecular docking-based virtual screening. C 2D structures of eight hits from virtual screening and the control compound 10074-G5. D Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay for evaluating c-Myc transcriptional inhibitory activity in HEK293T cells treated by eight candidate compounds. Error bars: mean ± SD, *P < 0.05. E Molecular docking predicted binding mode of compound D347-2761. Compound D347-2761 and the key residues for its binding were shown in stick models. The hydrogen bond interaction was depicted in red dotted line