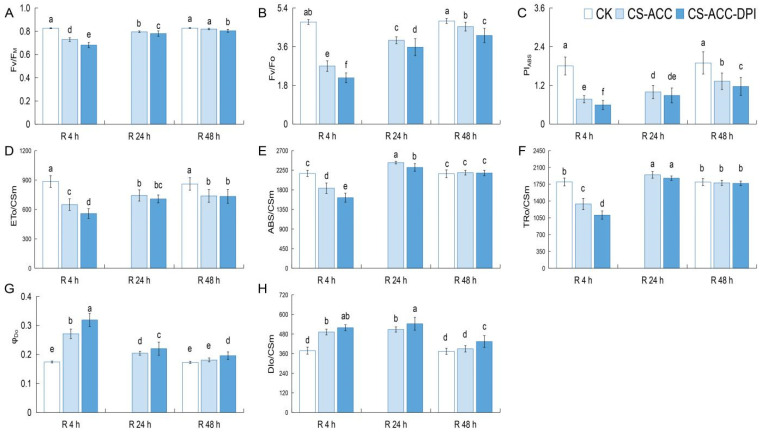
Figure 6.
RBOH-dependent signaling affected the different photosynthetic efficiency-related parameters FV/FM (A), FV/FO (B), PIABS (C), ETo/CSm (D), ABS/CSm (E), TRo/CSm (F), φDo (G), DIo/CSm (H) of PSII during recovery after CS-ACC in cucumber seedlings. CK: control, cucumber seedlings with no acclimation and at 25 °C during recovery; CS-ACC: cucumber seedlings were treated with a cold stress regime of 10 °C for 1 h, 25 °C for 1.5 h, and 1 °C for 3 h; CS-ACC-DPI: DPI was sprayed onto the seedlings during recovery after CS-ACC. CS-ACC: cold stress acclimation; R: recovery, 25 °C. FV/FM: maximum light energy conversion efficiency of the PSII reaction center; FV/FO: the potential photochemical activity of PSII; PIABS: performance index based on the absorbed light energy; ETo/CSm: the energy captured by per unit leaf section for electron transport; ABS/CSm: the light energy absorbed per unit leaf section; TRo/CSm: the energy flux captured by the active reaction center of PSII per unit leaf section; φDo: quantum ratio used for heat dissipation at t = 0; DIo/CSm: the energy of heat dissipation per unit leaf cross-section. The specific activity parameters accurately reflect the absorption, transformation, and dissipation of light energy by the photosynthetic organs when the fluorescence reaches its maximum. The different letters indicate significant differences as assessed by the Turkey HSD test (p < 0.05; n ≥ 4).