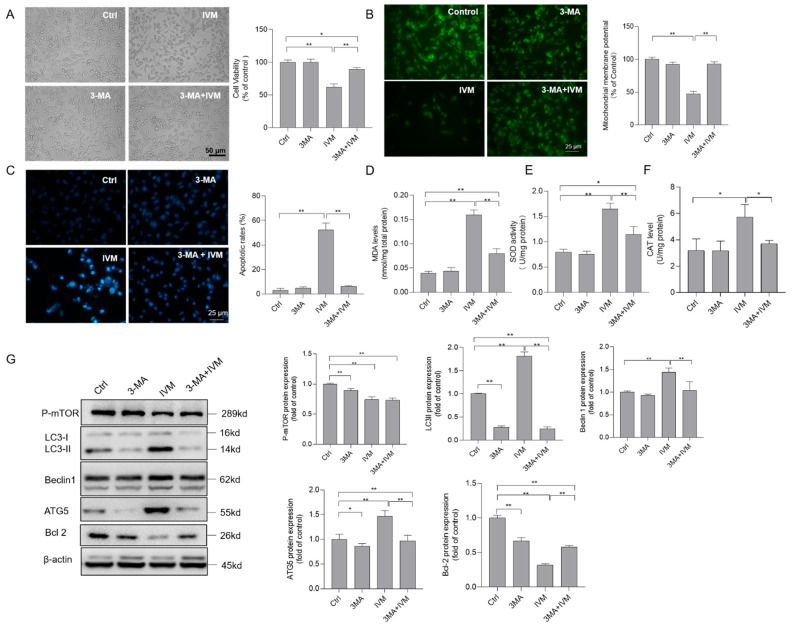
Figure 6.
Inhibition of autophagy decreases ivermectin (IVM)-induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in human SH-SY5Y cells. (A) cells were treated with IVM at 7.5 μM with or without 3-methyladenine (3-MA) (2 mM) for 24 h, changes in the cell morphology were observed, and cell viability was examined by the CCK-8 method. Bar = 50 μm. (B) changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential were examined using Rh123 staining. The representative gel (on the left) and quantitative analysis (on the right) are shown. Bar = 25 μm. (C) cell apoptotic rates were analyzed by using the Hoechst 33342 staining method. The representative gel (on the left) and quantitative analysis (on the right) are shown. Bar = 25 μm. (D–F) biomarkers of oxidative stress, including levels of MDA (D), activities of SOD (E), and CAT (F), respectively, were measured. (G) The expressions of autophagy-related proteins, including p-mTOR, LC3II, Beclin1, ATG5, and Bcl-2 proteins, were examined by Western blotting. Data shown are represented as the mean ± SD, from three independent experiments (n = 3); * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.