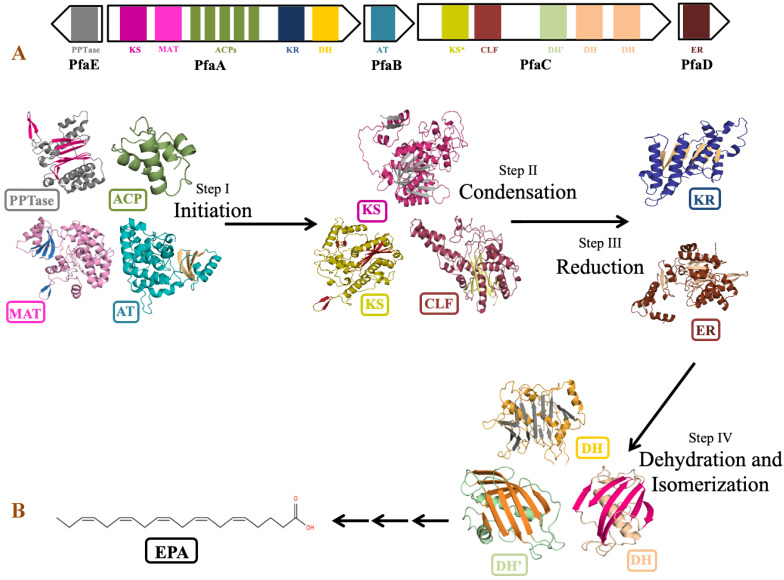
Figure 8.
Domain organization and role of catalytic domains of EPA biosynthetic gene cluster of Shewanella sp. N2AIL in PUFA synthesis. (A) The catalytic domains are organized in five open reading frames (ORFs) represented in the form of arrows and the domains are represented in the form of differently colored solid blocks. (B) The major steps in EPA biosynthesis include: (i) initiation involving activation of acyl carrier proteins (ACP) by phosphopantetheine transferase (PPTase) which carries acyl and malonyl substrates transferred by acyltransferase (AT) and malonyl CoA:ACP acyl transferase (MAT) domains for fatty acyl chain elongation, followed by several cycles of (ii) condensation involving ketoacyl synthase (KS) and chain length factor (CLF) domains, (iii) reduction by ketoacyl-ACP reductase (KR) domain and (iv) dehydration by dehydratase (DH) domain and FabA-type dehydratase. Finally, elongation process is completed by reduction of double bond by enoyl reductase (ER).