Figure 1.
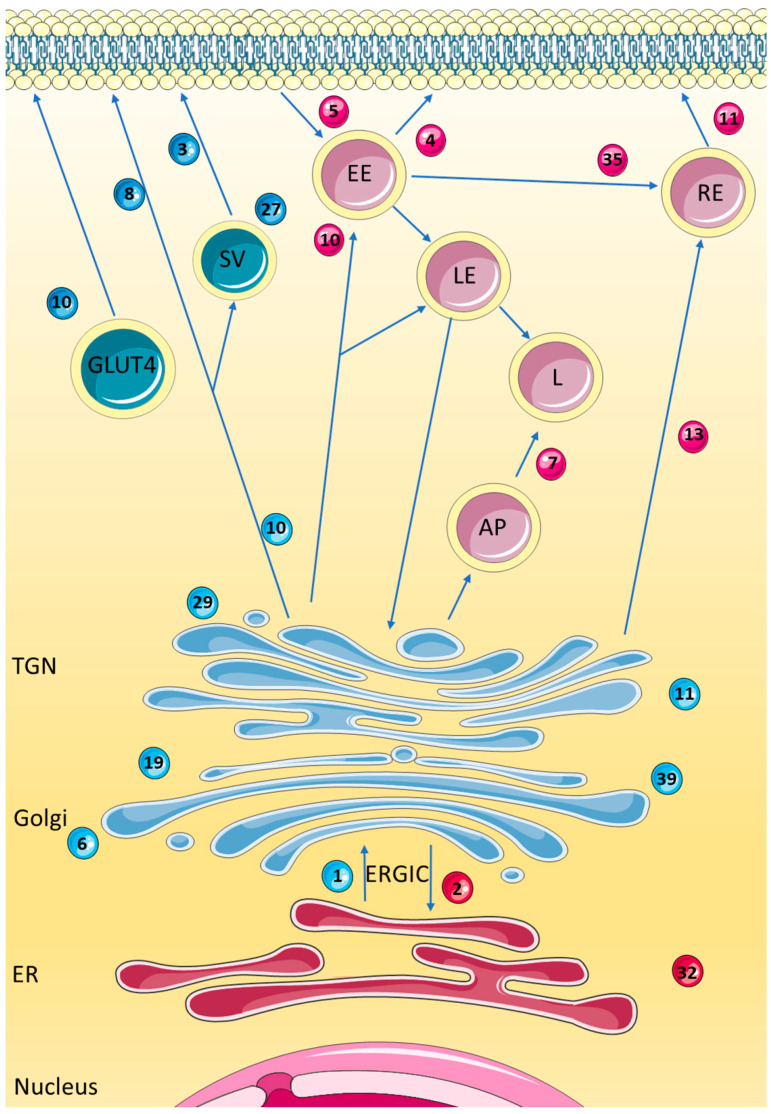
The Intracellular pathways and a selected number of Rab GTPases associated with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi, trans-Golgi network (TGN), and endosomal pathways. Rab1 and Rab2 are localised to the ER and Golgi, and play a role in the ER to Golgi apparatus trafficking pathway, via the endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). Rab3 is localised to synaptic secretory vesicles (SV) and the plasma membrane and is involved in exocytosis and neurotransmitter release. Rab4 has a role in protein recycling and transport to the plasma membrane and is localised to early endosomes (EE). Rab5 is localised to the EE and aids its fusion and formation. Rab6 is involved with regulating intra-Golgi trafficking. Rab7 is localised to the late endosome (LE), lysosome (L), and autophagosomes (AP) and is involved in the maturation and transport between these vesicles. Rab8 is associated with exocytosis from the TGN to the plasma membrane, with localisation to the plasma membrane and SV. Rab10 is localised to the ER, Golgi, endosomes, and GLUT4 vesicles and is involved in ER dynamics, endocytosis, and trafficking to the plasma membrane. Rab11 is also localised to the Golgi, as well as the recycling endosome (RE) and EE. Rab13 is involved in the TGN and RE to plasma membrane transport pathway. Rab19 has been shown to localise to the Golgi, however there is little known about its role. Rab27 is involved in exocytosis, localising to SV. Rab29 and Rab39 are both localised to the Golgi. Rab32 localises to the ER and mitochondria, with a role in mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy. Rab35 localises to the plasma membrane, and is involved in endocytic recycling. Rabs more strongly associated with secretory pathways are shaded in blue while those more strongly associated with endosomal pathways are shown in red. Adapted with permission from Hutagalung et al. 2022, American Physiological Society [7].