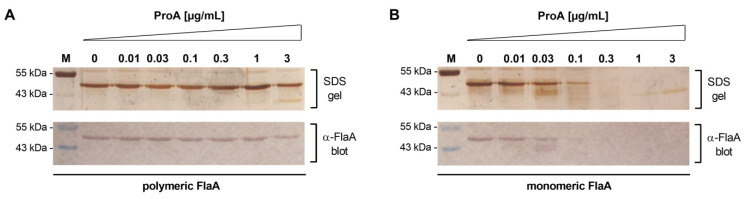
Figure 1.
ProA degrades monomeric flagellin. Flagella were isolated from L. pneumophila Corby and heated for 20 min to 70 °C for depolymerization. Polymeric (A) and monomeric (B) flagellin (10 µg/mL) was incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with indicated concentrations of purified ProA. Samples were separated in an SDS gel with subsequent protein silver staining. M: 1–5 µL of the PageRulerTM Prestained Protein Ladder by Thermo Scientific were used as a standard. Additionally, the samples were immunoblotted with a primary antibody against L. pneumophila FlaA and detected with an alkaline phosphatase antibody and NBT/BCIP substrate solution. While the polymeric form of flagellin is resistant against the proteolytic degradation by ProA, FlaA monomers were efficiently cleaved by the protease. Not more than one third of the initial substrate concentration was left after inoculation of FlaA monomers with 0.1 µg/mL ProA.