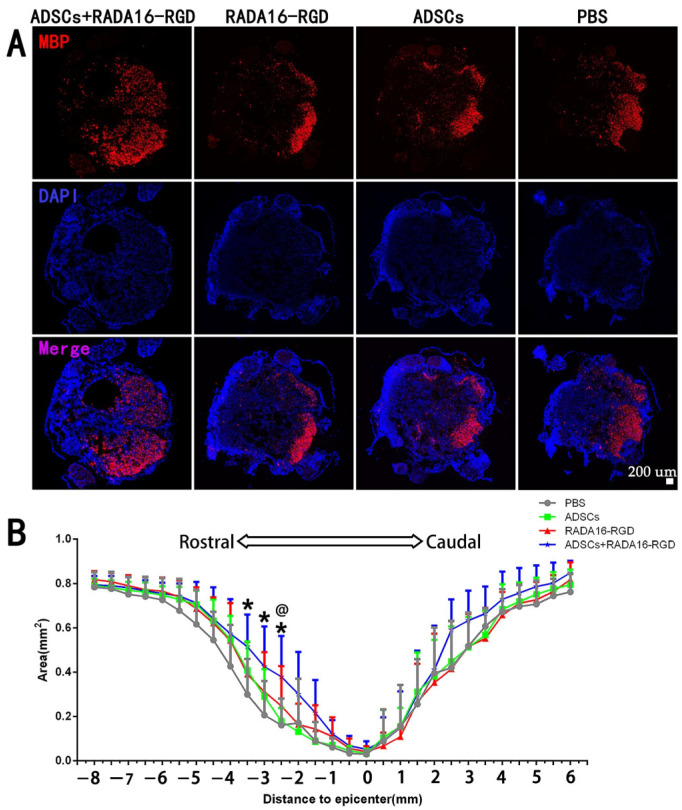
Figure 5.
ADSCs+RADA16-RGD transplantation inhibits axonal demyelination in rats with spinal cord injury. (A) At 8 weeks after ADSCs+RADA16-RGD transplantation, the area of MBP+ region at −2.5 mm rostral to the injury in spinal cord cross-sectional MBP antibody staining (red) was greater in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD group than in the RADA16-RGD and PBS groups. (B) Quantitative analysis of MBP at different distances from the injury center. There were significantly more MBP+ areas in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS group at −2.5 mm, −3 mm and −3.5 mm on the cephalic side of the injury center (p < 0.05); at −2.5 mm, there were significantly more MBP+ areas in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD group than in the ADSCs group (ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. PBS or ADSCs: p < 0.05) @ ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. ADSCs, * ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. PBS. @ p < 0.05, * p < 0.05. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6 per group). Scale bar = 200 µm. ADSCs: adipose stem cells; MBP: myelin basic protein; DAPI: 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. MBP (red): Alexa Fluor 647.