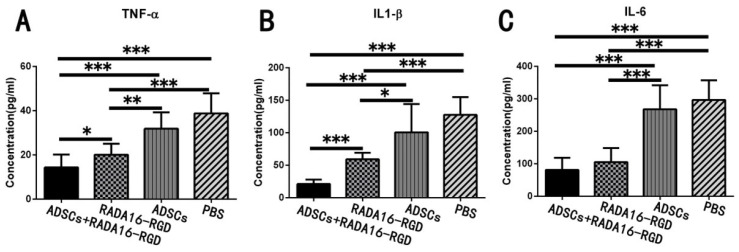
Figure 9.
ADSCs+RADA16-RGD transplantation inhibits the expression of inflammatory factors. The spinal cord samples were collected from rats 2 weeks after ADSCs+RADA16-RGD transplantation to detect the expression of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. (A) The expression of TNF-α was significantly lower in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS, ADSCs, and RADA16-RGD groups (ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. RADA16-RGD: p < 0.05, ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. ADSCs or PBS: p < 0.001). Moreover, the expression of TNF-α was significantly lower in the RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS and RADA16-RGD groups (RADA16-RGD vs. PBS: p < 0.001, RADA16-RGD vs. ADSCs: p < 0.01). (B) The expression of IL-1β was significantly lower in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS, ADSCs, and RADA16-RGD groups (ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. PBS, ADSCs, or RADA16-RGD: p < 0.001). Moreover, the expression of IL-1β was significantly lower in the RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS and ADSCs groups (RADA16-RGD vs. PBS: p < 0.001, RADA16-RGD vs. ADSCs: p < 0.05). (C) The IL-6 was significantly lower in the ADSCs+RADA16-RGD transplantation group than in the PBS and ADSCs groups (ADSCs+RADA16-RGD vs. PBS or ADSCs: p < 0.001), while it was significantly lower in the RADA16-RGD group than in the PBS and ADSCs groups (RADA16-RGD vs. PBS or ADSCs: p < 0.001). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). ADSCs: adipose stem cells; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta.