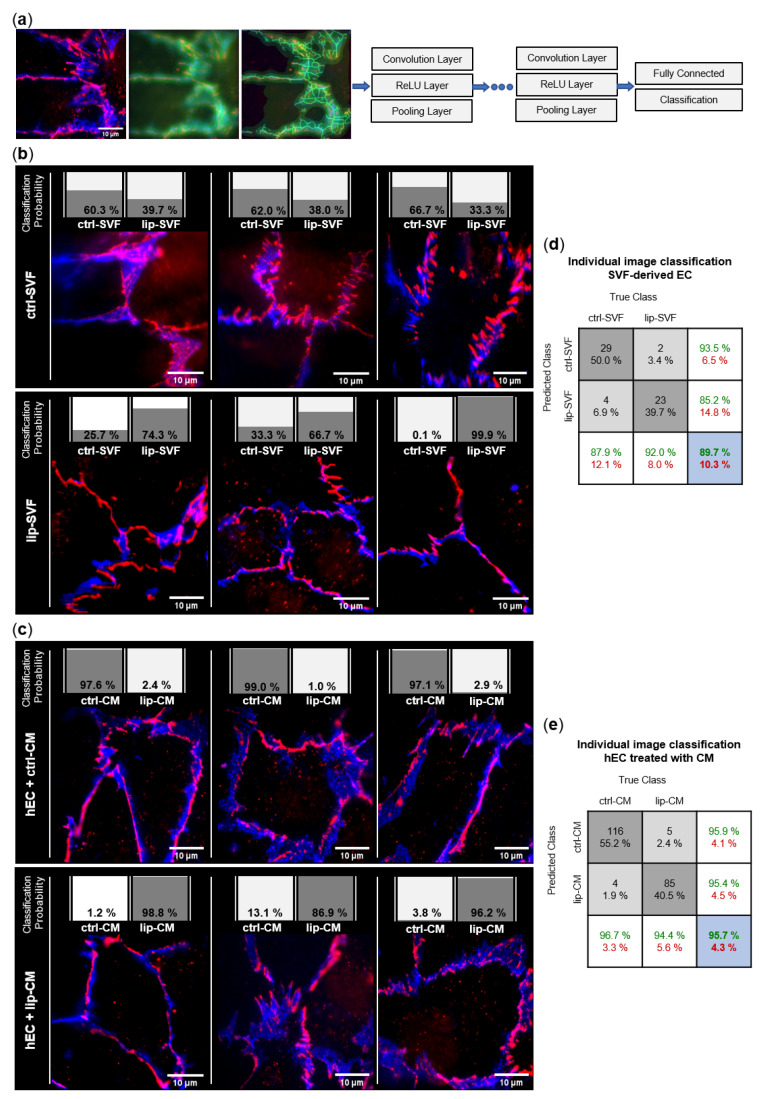
Figure 5.
Convolutional neural network (CNN)-based analysis of endothelial junction morphology. Endothelial cell (EC) junctions present in the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction (SVF) and human primary ECs (hEC) treated with SVF conditioned media (CM) of healthy (ctrl: n = 3) and lipedema (lip: n = 3) subjects were labeled with anti-CD31-AlexaFluor488 (blue) and anti-ZO-1-AlexaFluor647 (red) antibodies. The deep learning method CNN was applied to predict the classification of individual images to the ctrl and lip groups. (a) Image augmentation and architecture of the CNN network used for the classification of the image data. Each grouped CNN hidden layer includes a convolution layer, a rectified linear unit (ReLU) layer and a pooling layer. The output layers form a fully connected layer and a classification layer. (b) Classification of 3 representative images of ctrl and lip SVF-derived EC and (c) ctrl and lip-CM treated hEC. The individual classification probability of the regarding image is shown as a bar chart. (d,e) Confusion matrices of individual immunofluorescence image classification. Columns show the true class of images used in the data set. Rows show the predicted class calculated by the CNN. Dark grey boxes: absolute and relative correct classification; light grey boxes: absolute and relative false classification; white boxes: cumulative percentage of correct (green) and false (red) classification; blue: average correct (green) and false (red) classification accuracy.