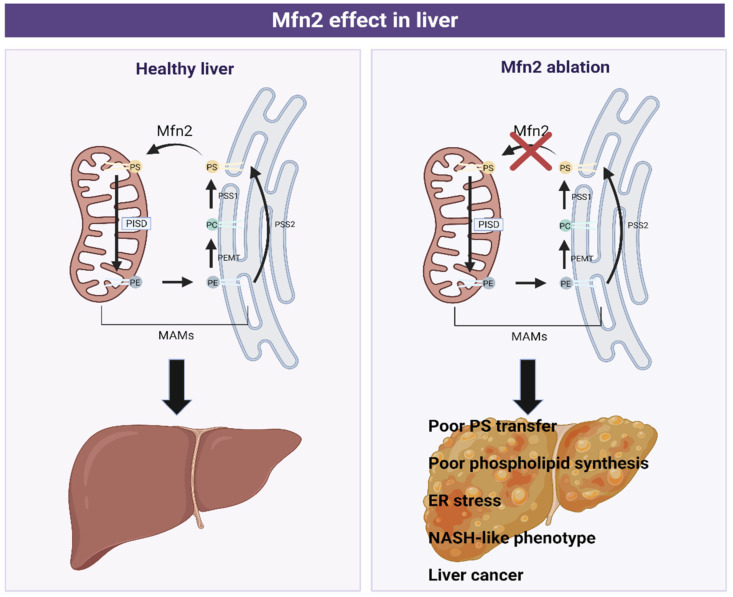
Figure 6.
Graphical scheme of phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis in Mitochondria-Associated Membranes (MAMs) in healthy (left) and pathological (right) liver conditions. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the ER is transformed to phosphatidylserine (PS) (catalyzed by the phosphatidylserine synthase 1 (PSS1)), which is transported to mitochondria by Mitofusin 2 (Mfn2). Here, it is converted to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase proenzyme (PISD), a protein located in the mitochondrial membrane. PE is then transferred to ER, where is converted to PC or PS, depending on the enzyme implicated, phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT), or phosphatidylserine synthase 2 (PSS2), respectively.