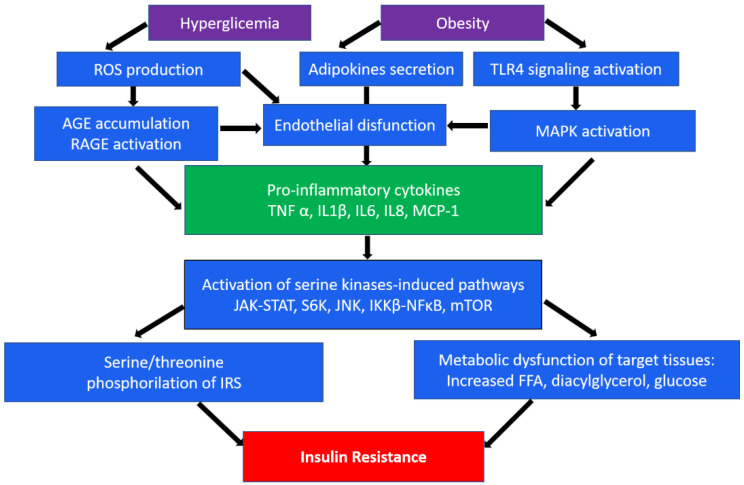
Figure 1.
A brief scheme of the main inflammatory mechanisms in the development of insulin resistance. ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; AGE, advanced glycation end-products; RAGE, AGE receptor; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; IL, interleukins; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; JAK-STAT, Janus kinase signal transducers as well as activators of transcriptional signaling pathway; S6k, ribosomal protein S6 kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB pathway; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; FFA, free fatty acids.