Figure 1.
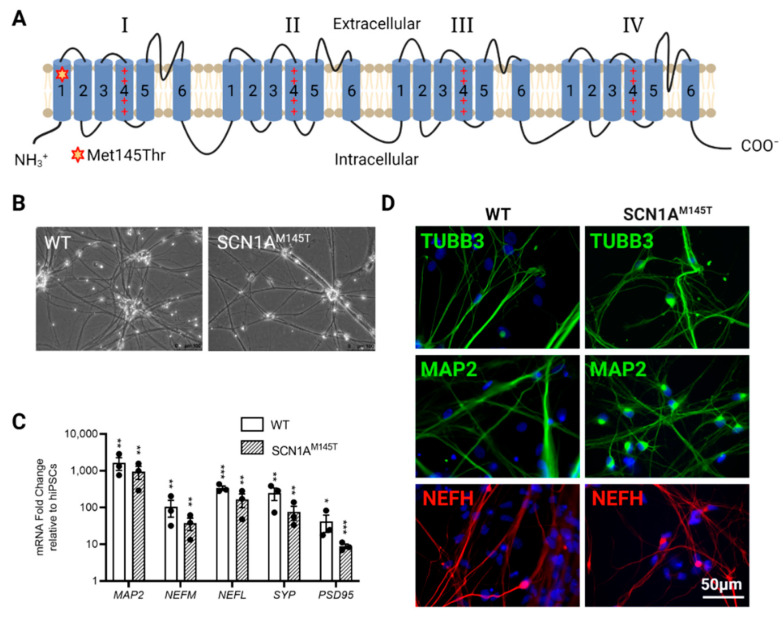
Characterization of idNs. (A) Representation of NaV1.1 channel. The star in segment 1 of domain I shows the localization of the mutated aminoacid (Met145Thr). The relative missense mutation c.434T > C is found in the exon 3 of the translated sequence. (B) Bright-field images of idNs from WT and SCN1AM145T-iPSCs (20× magnification). (C) Differentiated idNs show high expression levels of neuronal specific genes such as MAP2, NEFM, NEFL, SYP and PSD95 compared to their undifferentiated counterparts (iPSCs). GAPDH was used as a housekeeping control. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three biological replicates (black dots), * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, t-test has been calculated vs. expression in iPSCs. (D) Immunostaining of neuronal markers TUBB3 (neurites marker), MAP2 (cell body and dendrites marker), and NEFH (axonal marker) in WT and SCN1AM145T idNs. DAPI nuclear counterstain is shown in all images in blue (63× magnification).