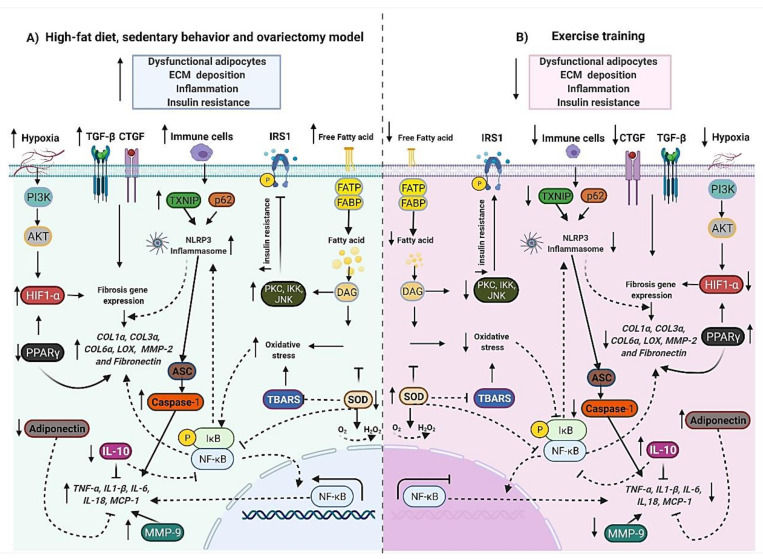
Figure 5.
The molecular landscape of adipose tissue extracellular matrix remodeling in response to dietary patterns and exercise training. (A) The high-fat diet, sedentary behavior, and ovariectomy model induces dysfunctional adipocytes (↑ lipid accumulation), ECM deposition (↑ pro-fibrotic gene expression), inflammation (↑ NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, pro-inflammatory cytokines, macrophage and MMP-9), oxidative stress (↑ ROS production and hiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS)), and insulin resistance (↑ insulin and blood glucose levels). (B) Exercise attenuates dysfunctional adipocytes (↓ lipid accumulation), ECM deposition (↓ pro-fibrotic gene expression), inflammation (↓ NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, pro-inflammatory cytokines, macrophage, and MMP-9), oxidative stress (↓ ROS production and hiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS)), ↑ antioxidant activity (superoxide dismutase (SOD)) and insulin resistance (↓ insulin and blood glucose levels). Biorender web-based software was used to create the figure (License Number SQ23TBWSCJ).