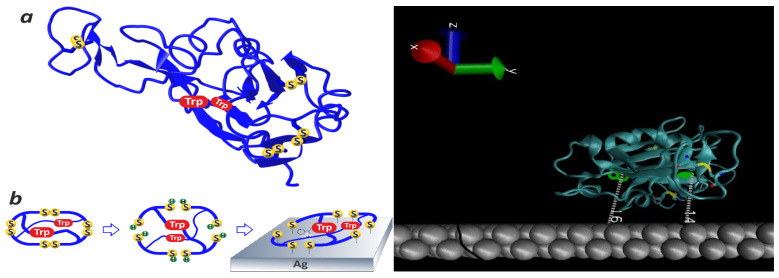
Figure 3.
Left: A sketch illustrating the method for fabricating a metal–dielectric microcavity consisting of a dielectric protein globule of the RBD and the metal surface of the SERS-active substrate. The reduction of all four disulfide bonds of the RBD protein results in the formation of an additional eight free sulfhydryl groups capable of forming strong chemical bonds with silver atoms. The unfolding of the protein globule as a result of disulfide bond reduction leads to spatial approximation between the tryptophan (Trp) residues and the surface of the SERS-active substrate and the dominance of Trp in the SERS spectrum (see the data presented in Section 3.1 below). Right: A sketch of the structure of the native RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 S glycoprotein applied onto the silver surface of the SERS-active substrate. The distances between the surface of the SERS-active substrate and two Trp residues of the RBD amino acid sequence located deep in the protein globule are indicated. The data were calculated from the atomic coordinates of the three-dimensional structure of the RBD protein reported in [13].