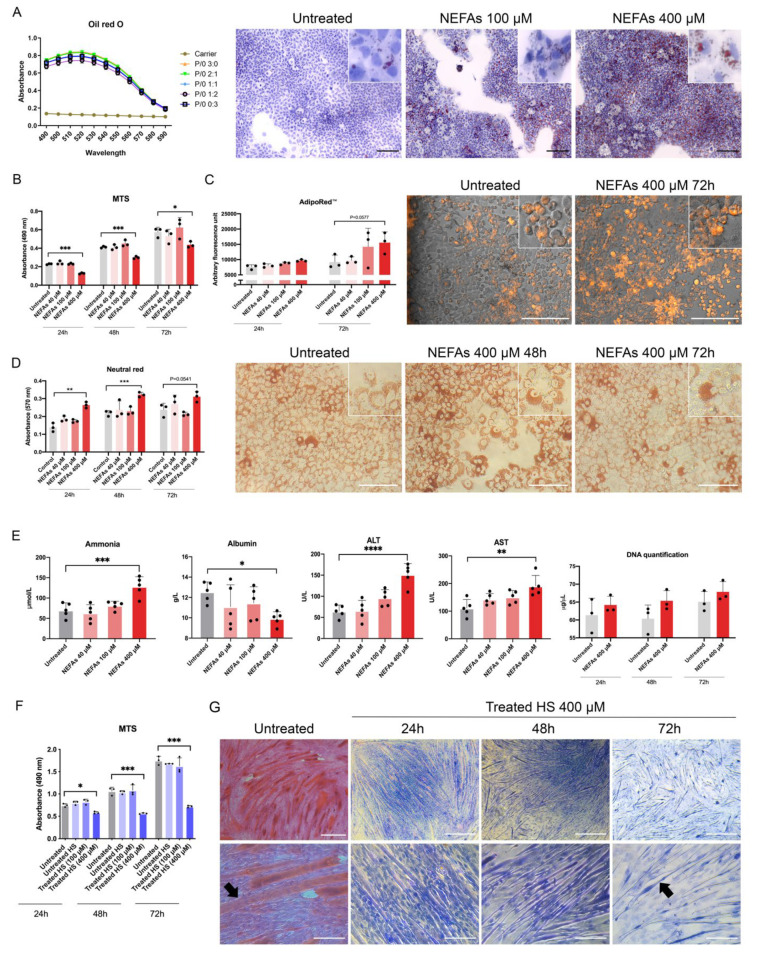
Figure 2.
2D in vitro models of fatty hepatocytes (AML12) and sarcopenic skeletal muscle cells (C2C12). (A) Absorbance signal of various internalized non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) combinations assessed by Oil-red-O assay (P = palmitic acid; O = oleic acid) after 48 h. Scale bar = 500 µm. (B) Metabolic activity of AML12 cells challenged with various concentrations of NEFAs measured by MTS assay. (C) Intracellular lipid accumulation was assessed quantitatively (fluorimeter) and qualitatively (confocal microscopy) by AdipoRed™ assay. Scale bar = 100 µm. (D) AML12 cells’ lysosomal re-arrangement upon NEFAs challenge assessed quantitatively (spectrometer) and qualitatively (light microscopy) by Neutral red assay. Scale bar = 100 µm. (E) Biochemical analyses of the supernatant of AML12 challenged with NEFAs for 72 h assessed by clinical standard procedures. (F) Metabolic activity of C2C12 cells incubated with supernatant from fatty AML12 cells. (G) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of C2C12 cells incubated with supernatant from fatty hepatocytes. Black arrows indicate fused myoblasts (myotubes). Scale bar top panel = 400 µm, and bottom panel = 100 µm. The results are expressed as mean values ± SEM and compared using one-way analysis of variance followed by post hoc tests when appropriate. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001. P: palmitic acid; O: oleic acid; NEFAs: non-esterified fatty acids; MTS: 3-[4,5,dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-5-[3-carboxymethoxy-phenyl]-2-[4-sulfophenyl]-2H-tetrazolium; ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase; HS: hepatocytes’ supernatant.