Table 1.
Nomenclature, structure, and characteristics of the four synthetic cannabinoids included in this review.
| AB-CHMINACA | MDMB-CHMICA | 5F-MDMB-PINACA * | ADB-CHMINACA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name | N-(1-Amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide | Methyl 2-({[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate | Methyl 2-{[1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1Hindazole-3-carbonyl]amino}-3,3-dimethylbutanoate | N-(1-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide |
| Street names ** | Aromatic Pot Pourri, Jamaican Gold Supreme, Bonzai Citrus, Blaze, Bubblegum, Manga Xtreme, Matt Hardener, Aura mystic Bulc | Godfather, CUSHCottonCandy, KUSHSecondGereration, KUSHherbal incense, Ninja, Sirius, SKIHIGH, CRITICAL haze |
ANNIHILATION, BLACK MAMBA ULTRA, Blueberry Blitz, CHERRY BOMB, Dutchy, EXODUS FORMULA 6-A, Sky High, Spike 99 ULTRA, and Vanilla Ice | ADB-CHMINACA, MAB-CHMINACA |
| Molecular formula | C20H28N4O2 | C23H32N2O3 | C20H28FN3O3 | C21H30N4O2 |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) |
356.5 | 384.5 | 377.5 | 370.5 |
| Structure |
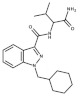 Linked group: methyl amino butanone (AB) Tail: cyclohexylmethyl (CHM) Core: indazole (INA) Linker: carboxamide (CA) |
 Linked group: methyldimethylbutanoate (MDMB) Tail: cyclohexylmethyl (CHM) Core: indole (I) Linker: carboxamide (CA) |
 Linked group: dimethyl methyl butanoate (MDMB) Tail: pentyl (P), with a fluoro moiety at the position 5 Core: indazole (INA) Linker: carboxamide (CA) |
 Linked group: dimethylaminobutanone (ADB) Tail: cyclohexylmethyl tail (CHM) Core: indazole (INA) Linker: carboxamide (CA) |
| Pharmacology and toxicology | Full and partial agonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively; 11–58 times more potent than THC [33] |
Potent and full agonist of the CB1 receptor and agonist at the CB2 receptor; 400 times more potent than THC, two times more potent than AB-CHMINACA [34] |
Potent full agonist at the CB1 and CB2 receptor; 289 times more potent than THC, 17 times more potent than MDMB-CHMICA [35] |
Potent and full agonist of the CB1 receptor and agonist at the CB2 receptor; 270 times more potent than THC [36] |
| Detection and evaluation by the EMCDDA | First detected: February 2014 (Riga, Latvia) First notified to the EMCDDA: April 2014 Risk-assessed by the EMCDDA in 2017 |
First detected: August 2014 (Hungary) First notified to the EMCDDA: September 2014 Risk-assessed by the EMCDDA in 2016 |
First detected: September 2014 (Hungary) First notified to the EMCDDA: January 2015 Risk-assessed by the EMCDDA in 2017 |
First detected: Synthesis of ADB-CHMINACA was first described in a 2009 patent by Pfizer First notified to the EMCDDA: September 2014 Risk-assessed by the EMCDDA in 2017 |
| Psychological and behavioral effects | Duration of the effect: 1–2 h after smoking Effects: cannabis- and THC-like (relaxation, confusion, anxiety…); psychotic episodes and aggressive behaviors have also been reported |
Duration of the effect: 120 min after smoking Effects: more pronounced in comparison to cannabis; most common paranoia, euphoria, visual hallucinations, and anxiety |
Duration of the effect: 1–2 h after smoking. Effects lasting more than 10 h have been described Effects: cannabis- and THC-like (relaxation, confusion, anxiety); psychotic episodes and aggressive behaviors have also been reported. |
Effects: cannabis- and THC-like (relaxation, confusion, anxiety…); psychotic episodes and aggressive behaviors have also been reported |
| Some analytical identification techniques used based on the EMCDDA | GC-MS; FTIR-ATR; HPLC-TOF; NMR; LC-MS; UV-VIS; LRMS; HRMS; DART-MS [37] | NMR and HPLC-DAD for quantification in products. LC-MS/MS for detection in biological samples [38] | HPLC-DAD for quantification in products. LC-MS/MS for detection in biological samples [39] | In products: GC-MS, LC-QqQ-MS/MS, GC-TOF-MS, GC-EI-MS, NMR, LC-MS/MS, IR, UV In biological samples: LC-QqQ-MS/MS, LC-MS/MS, LC-QTRAP-MS/MS, GC-MS, LC-QTOF-MS [40] |
* Also known as 5F-ADB; **: due to the frequently changing cannabinoid content of the product, it is possible that the name does not match current SC content. Abbreviations: DART-MS: direct analysis in real time; FTIR-ATR: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy attenuated total reflectance; GC-EI-MS: gas chromatography/electron ionization mass spectrometry; GC-MS: gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; GC-TOF-MS: gas chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry; HPLC-DAD: high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector; HPLC-TOF: high-performance liquid chromatography time-of-flight; HRMS: high-resolution mass spectrometry; IR: infrared spectroscopy; LC-MS: liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; LC-MS/MS: liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry; LC-QqQ-MS/MS: liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry; LC-QTOF-MS: liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry; LC-QTRAP-MS/MS: ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with QTRAP mass spectrometry; LRMS: low-resolution mass spectrometry; NMR: nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy; UV-VIS: ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy.
