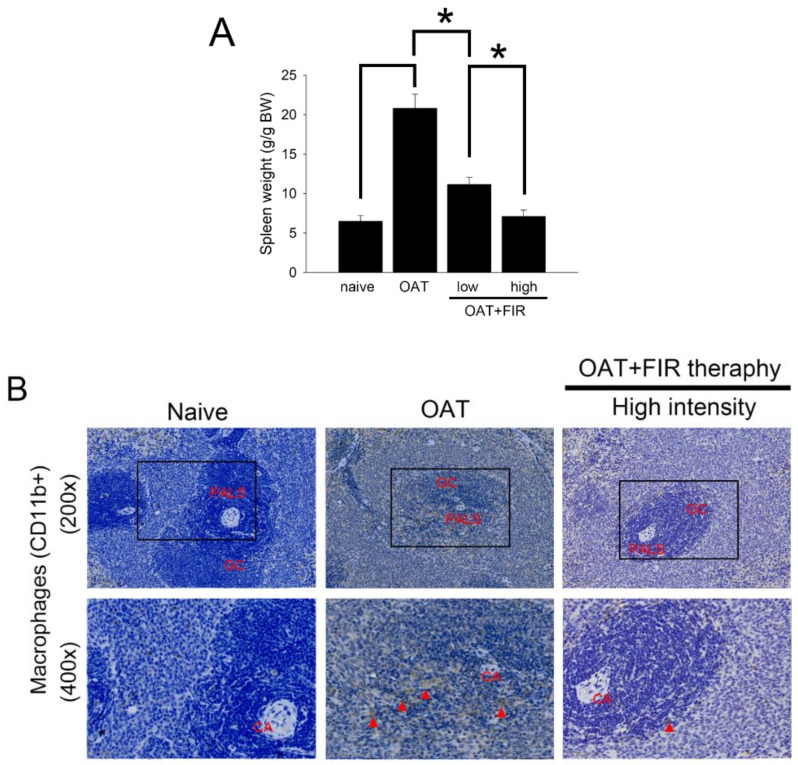
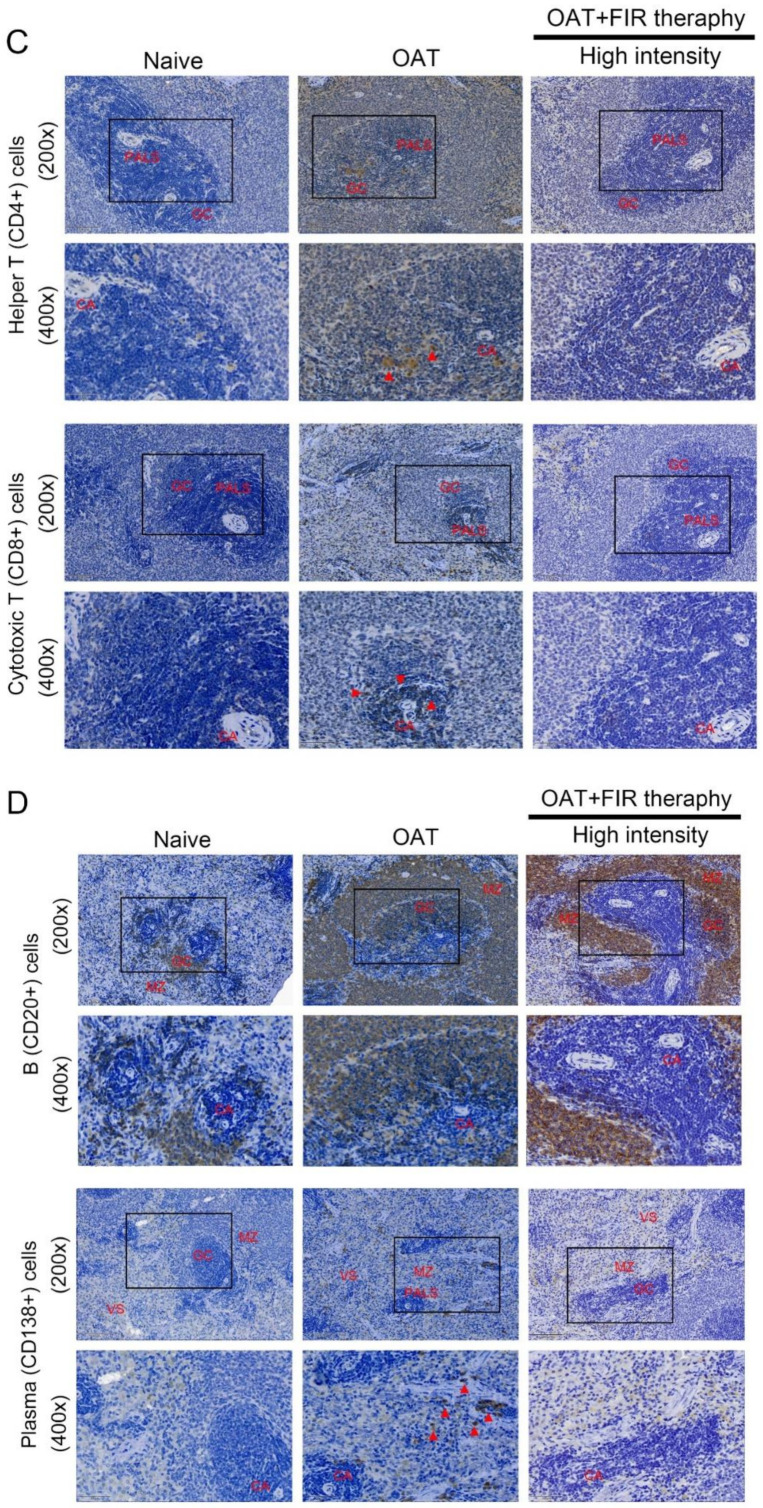
Figure 3.
FIR therapy decreased splenic T lymphocytes, plasma cells, B lymphocytes, and macrophages activation in the OAT-ACI/NKyo rats. (A) The spleens were dissected from experimental rats after they were sacrificed. The weight of the spleen was analyzed and presented in a bar graph in g/g BW. The results are expressed as the mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 was taken into consideration statistically considerable. (B) Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze the accumulation of splenic CD11b+ macrophages in the OAT-recipient ACI/NKyo rats (CA, central artery; PALS, periarterial lymphatic sheath; GC, germinal center;). The red triangle arrow heads are CD11b+ macrophages. The images in the column are 200× and 400× magnification, respectively. (C) Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze accumulation of splenic CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and CD4+ helper T cells in the recipient rats. The images are presented in 200× and 400× magnification. The CD4+ and CD8+ cells are indicated by red arrow heads. (D) The splenic CD20+ B cells and CD138+ plasma cells accumulation in the OAT-recipient rats (MZ, mantle zone and VS, venous sinuses). The images in the column are 200× and 400× magnification, respectively. The red triangle arrow heads indicate CD138+ cells. The cell nuclei were counted with hematoxylin.