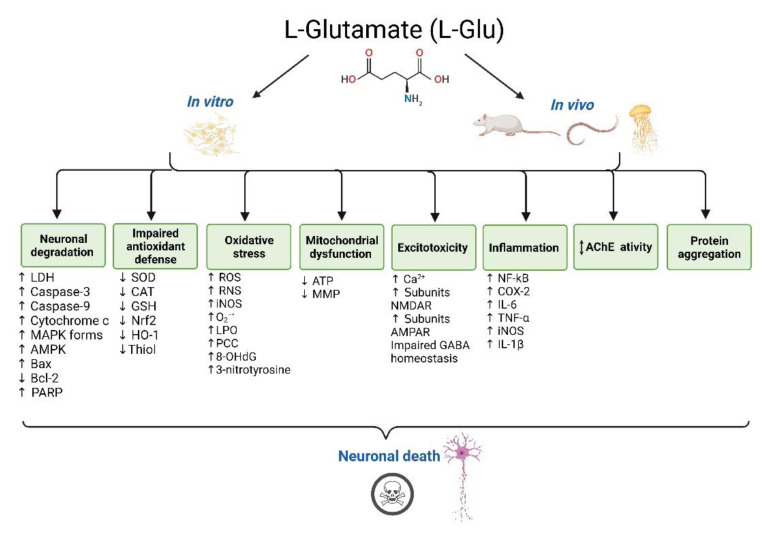
Figure 4.
Schematic summary of the shared neurotoxicity mechanisms of L-Glu reported from in vitro and in vivo model studies. Abbreviations: AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; AMPK, 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP, adenosine diphosphate; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Ca2+, calcium ion; CAT, catalase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; GSH, glutathione; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; iNOS, nitric oxide synthase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LPO, lipid peroxidation; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP, mitochondrial membrane potential; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; O2−•, superoxide; 8-OHdG, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine; PARP, poly (adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose) polymerase; PCC, protein carbonyl content; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-α.