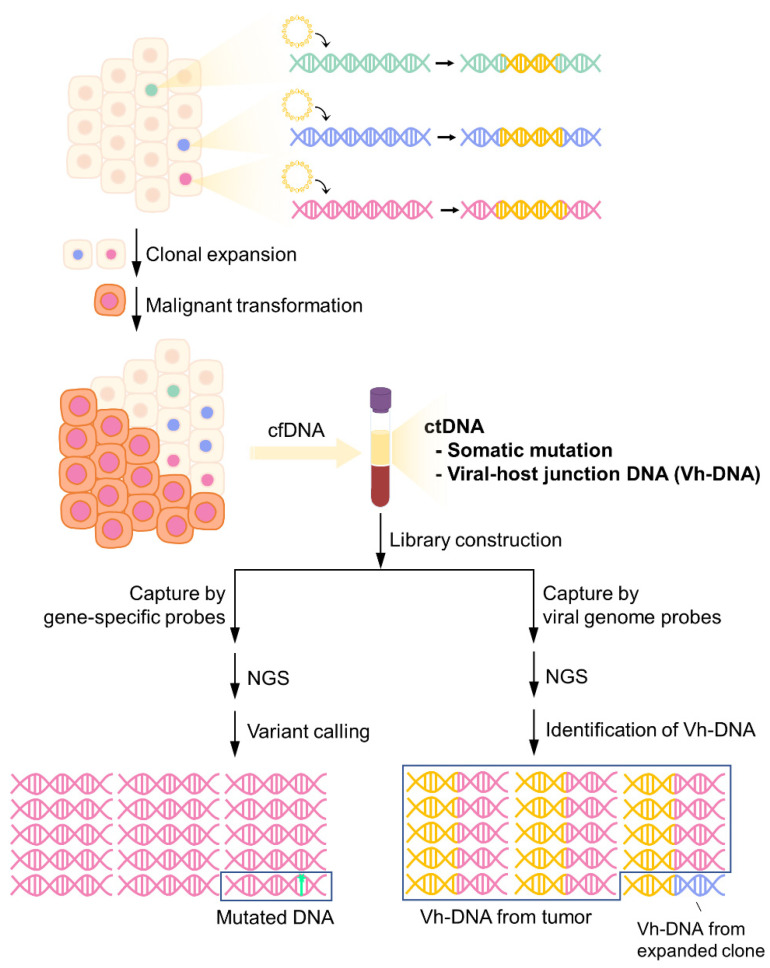
Figure 1.
Detection of somatic mutations and vh-DNA from cfDNA by targeted-NGS. Virus DNA integrates into the host genome during infection. Infected cells may undergo clonal expansion due to insertional mutagenesis and eventually become tumor cells through the accumulation of somatic mutations. As cell-free tumor markers, both tumor-specific somatic mutations and vh-DNA can be detected in plasma. However, the frequency of somatic mutations is low in cfDNA, while tumor-released vh-DNA is the main component of the total population of vh-DNA.