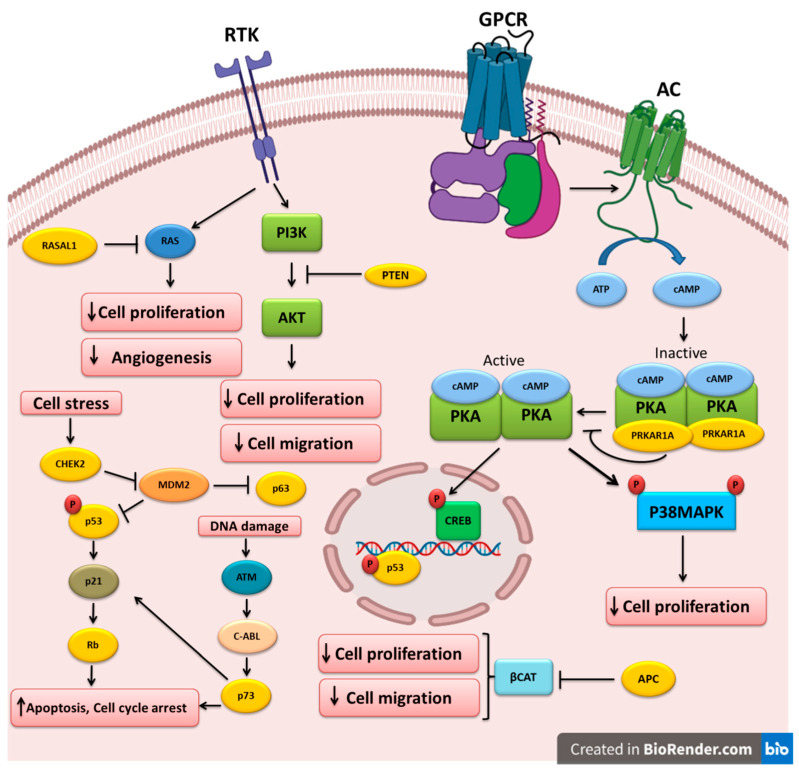
Figure 2.
Key tumor-suppressor genes and their related pathways in thyroid cancer. Growth factors bind to their receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) and activate the PI3K and RAS pathways that could be inhibited by PTEN and RASAL1, respectively. Cell stress triggers CHEK2, which in turn downregulates MDM2, leading to the upregulation of the p53 and p63 tumor-suppressors. P53 can also increase RB expression. DNA damage could lead to p73 upregulation and apoptosis induction. APC inhibits beta-catenin, leading to the inhibition of cell proliferation and migration. Ligand binding to G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) induces G-protein and adenylyl cyclase (AC), which increases cAMP and PKA activation. PRKAR1A mutations could cause PKA hyperactivation and cell proliferation induction.