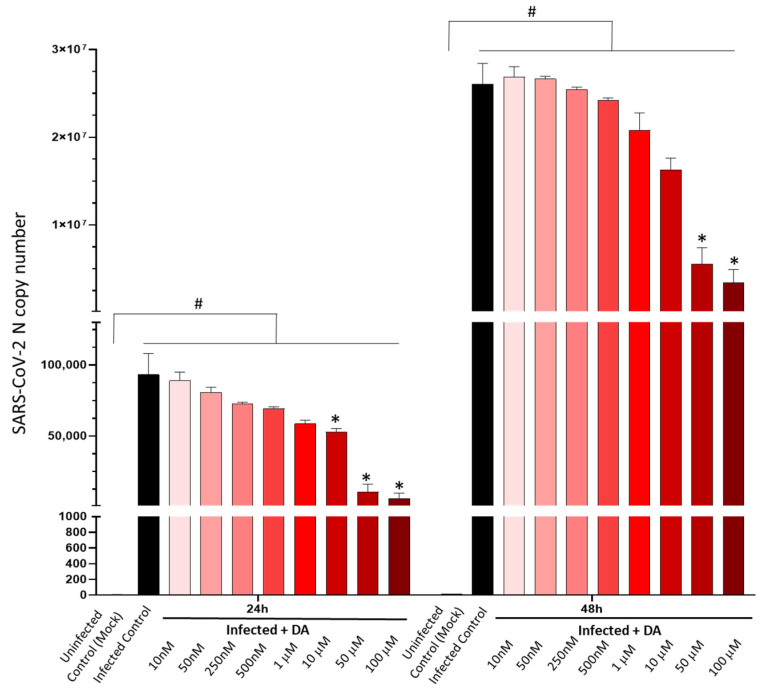
Figure 1.
Dose- and time-related effects of dopamine in SARS-CoV-2 replication. Dopamine (DA) dose-dependently reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication at 24 and 48 h post-infection in CaLu-3 epithelial lung cells. Significant antiviral effects of DA occur in the micromolar range (10–100 μM). While the antiviral effects of the 10 μM DA dose lose significance at 48 h, DA at 50–100 μM doses produces a significant antiviral effect that persists at 48 h, exceeding 80% reduction in viral titers (SARS-CoV-2-N gene RNA levels). SARS-CoV-2 was not detected in the Uninfected Control (Mock). Results correspond to the absolute viral copy number of the SARS-CoV-2 N gene from cell supernatants that were quantified through a single-step, real-time, RT-qPCR by referring to a standard curve from RT-qPCR Ct values (IDT, Coralville, IA, USA). Results are presented as mean ± SEM from at least n = 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. # p < 0.05 vs. Uninfected Control (Mock); * p < 0.05 vs. SARS-CoV-2-Infected Control.