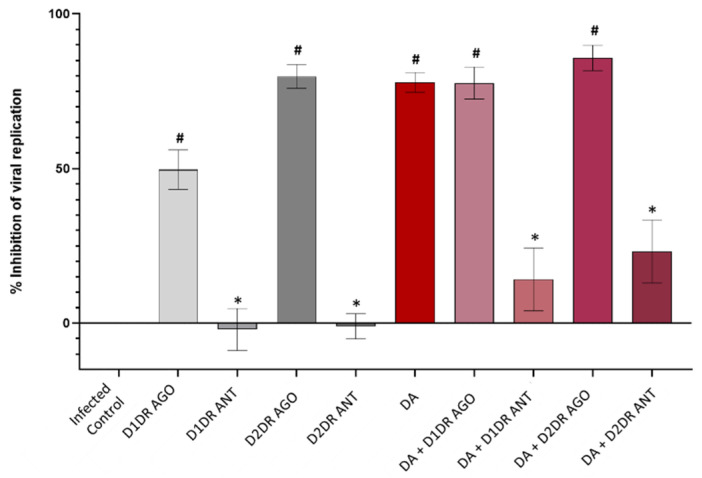
Figure 2.
Effects of the D1 and D2 dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists in SARS-CoV-2 replication. D1DR and D2DR agonists (10 μM) reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication at 48 h post-infection, recapitulating the antiviral effect of DA (50 μM), which is instead reversed by D1DR and D2DR antagonists (10 μM). In detail, while the antiviral effect of the D1DR agonist alone is modest, reaching 50% of viral replication inhibition, the D2DR agonist either alone or in combination with DA, produces a robust antiviral effect (>80% inhibition of detectable viral RNA) which recapitulates and slightly surpasses that produced by DA alone. On the other hand, administration of either D1DR or D2DR antagonists alone favors SARS-CoV-2 replication, meanwhile occluding the antiviral effects of DA in the co-administration protocol. Values are expressed as percent (%) inhibition of viral replication, calculated as “1–SARS-CoV-2 N gene copy number of SARS-CoV-2-infected treated cells/SARS-CoV-2 N gene copy number of SARS-CoV-2-infected Control (untreated) cells”, with SARS-CoV-2 Infected Control corresponding to 0% Inhibition of viral replication. The absolute viral copy number of the SARS-CoV-2 N gene from cell supernatants was quantified through a single-step, real-time, RT-qPCR by referring to a standard curve from RT-qPCR Ct values (IDT, Coralville, IA, USA). Results are presented as mean ±SEM from at least n = 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. # p < 0.05 vs. SARS-CoV-2-Infected Control; * p < 0.05 vs. DA 50 μM.