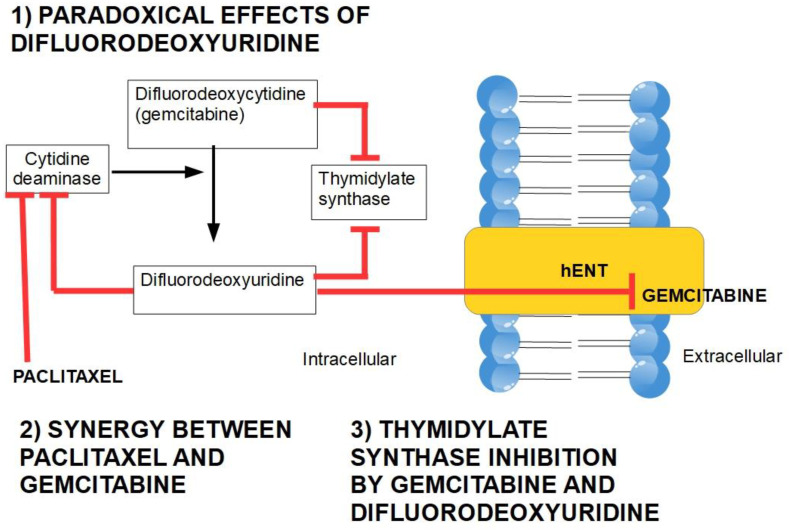
Figure 7.
Difluorodeoxyuridine exerts inhibitory effects on cytidine deaminase, thus increasing gemcitabine’s intracellular effects, and it competitively antagonizes gemcitabine intake through hENT. A lower activity of cytidine deaminase is paralleled by a higher cytotoxicity of gemcitabine. This diagram is based on references [248,249,252,253,254,255]. The figure also shows that both gemcitabine and its metabolite difluorodeoxyuridine have the ability to inhibit thymidylate synthase (TS), with further toxicity [256,257]. TS inhibition by 5-FU increased gemcitabine sensitivity [258,259]. Tymidylate synthase inhibition seems to be a valid alternative to gemcitabine in PDAC [260,261].