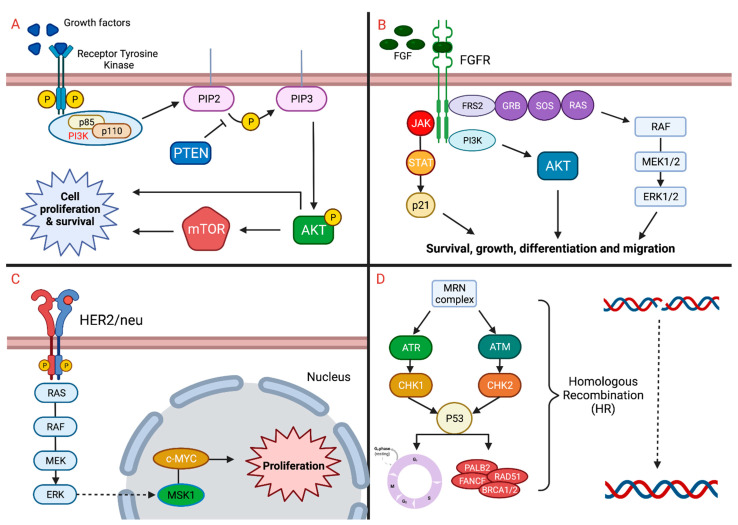
Figure 1.
Various genomic pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of urothelial carcinoma. Panel (A) represents the PI3K, AKT, and mTOR pathway. Panel (B) represents the FGFR pathway and its involvement with the JAK/STAT, PI3K, and MAP kinase pathways. Panel (C) represents the HER2 pathway and its involvement with the MAP kinase pathway. Panel (D) represents the homologous recombination alterations and how they lead to pathogenesis of urothelial carcinoma.