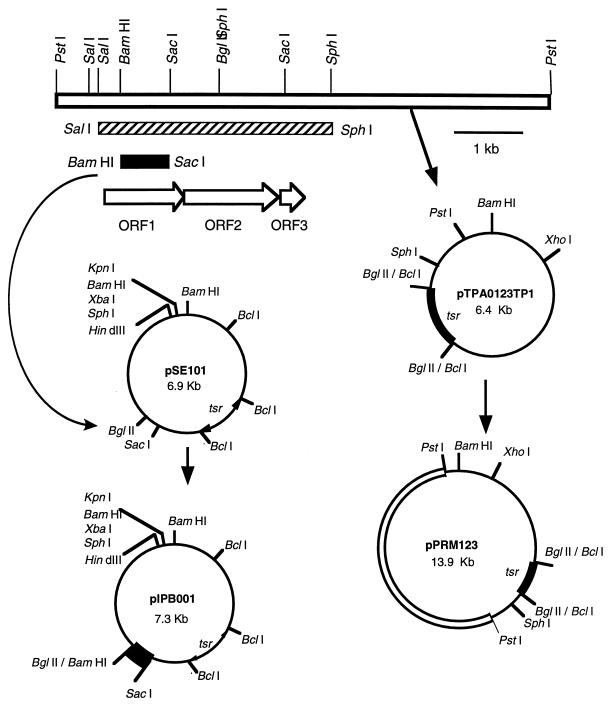
FIG. 2.
Construction of plasmids used for complementation and gene inactivation experiments. The 7.5-kb PstI fragment (open box) prepared from cosmid pPRM30 containing essential PKS genes for PRM A biosynthesis was ligated with pTPA0123TP1, which was digested with PstI and treated with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase. S. lividans TK23 (14) was transformed with the ligation mixture. A recombinant plasmid (pPRM123) was screened among the thiostrepton-resistant transformants and used to transform a PRM A-nonproducing mutant, JN51. For gene inactivation experiments, pSE101 (a shuttle vector constructed with pIJ702 and pUC19) (3) was digested with BglII and SacI, and the resulting large fragment (6.6 kb) was ligated with the 0.7-kb BamHI-SacI fragment (black box) carrying the internal region of ORF1. The ligation mixture was used to transform S. lividans TK23. A recombinant plasmid (pIPB001) was isolated from the transformant and used to transform A. verrucosospora E40. The 3.5-kb SalI-SphI fragment (hatched box) used for sequencing analysis is also shown.