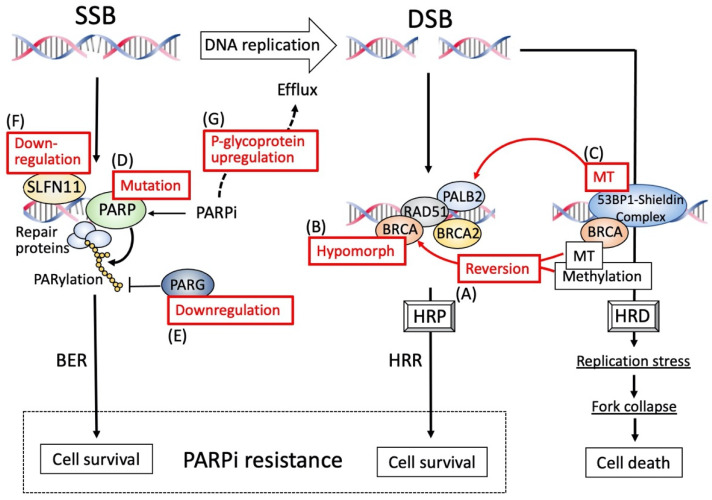
Figure 6.
Various factors that involve PARPi resistance. PARPi resistance is conferred by proper repair of single strand breaks (SSBs) via PARP-dependent base excision repair (BER) or double strand breaks (DSBs) via homologous recombination repair (HRR), whereas DSBs cannot be repaired in the presence of the 53BP-Shieldin complex, which sequesters the PALB2-BRCA2-RAD51 complex, alternative repair molecules for HRR, conferring the HRD phenotype, leading to replication stress-induced fork collapse and cell death. Of various factors involved in PARPi resistance, seven representative causes are shown by numbers in red boxes that function to support the BER or HRR pathway. The acronyms are defined as follows: HRD, homologous recombination deficiency; HRP, homologous recombination proficiency; PALB2, partner and localizer of BRCA2; PARG, poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase; RAD51, RAD51 recombinase; SLFN11, Schlafen family member 11; 53BP1, p53-binding protein 1.