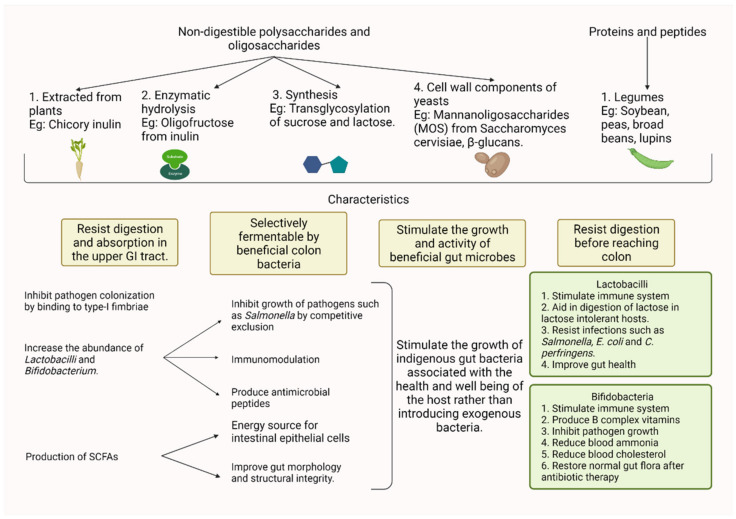
Figure 4.
Prebiotics are polysaccharides or oligosaccharides capable of resisting digestion and absorption in the proximal intestine and is selectively fermented by caecal and colonic bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, thus increasing their abundance in host gut. Prebiotics act as decoy receptors for the binding of pathogens, thus preventing their attachment to the host intestinal cells. Prebiotics also serve as a substrate for the production of SCFAs which serve as energy source for the intestinal epithelial cells. Created with Biorender.com (26 April 2022).