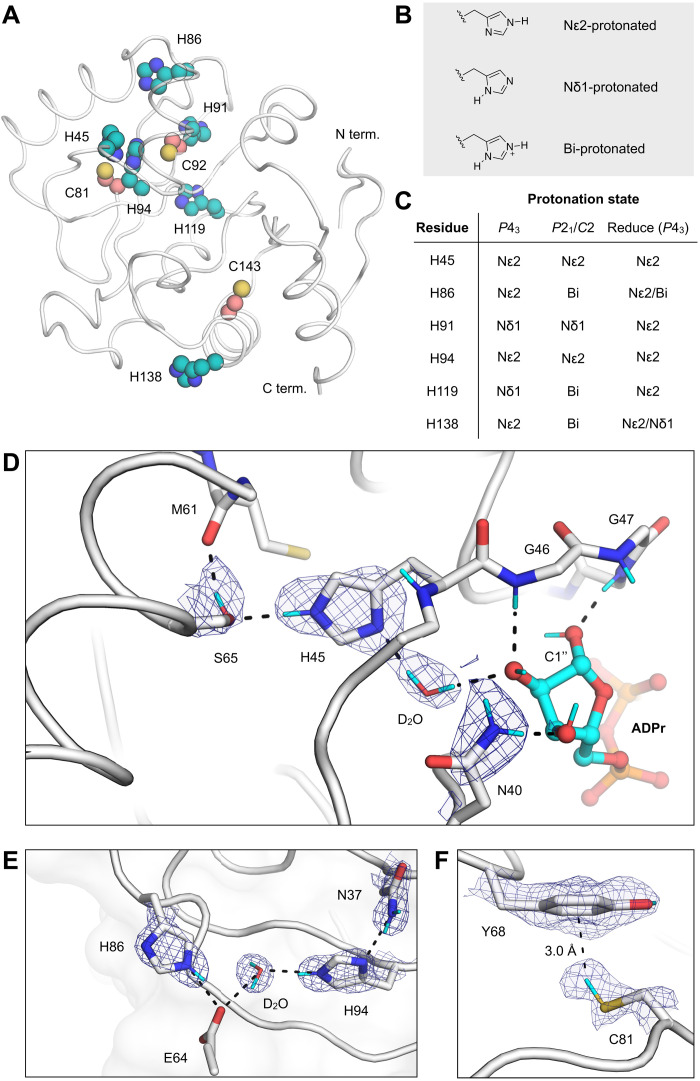
Fig. 3. Protonation states of Mac1 residues assigned by neutron diffraction.
(A) The location of histidine (teal spheres) and cysteine (salmon spheres) residues mapped onto the Mac1 structure (PDB code 7KQO). (B) Chemical structures showing the three possible protonation states of histidine. (C) Histidine protonation states assigned on the basis of NSL density maps (maps are shown in fig. S5). The protonation states assigned to the high-resolution P43 x-ray structure (PDB code 7KQO) by the program Reduce are also shown. (D) NSL density maps reveal the hydrogen bond network connecting His45 and ADPr in the C2 structure (PDB code 7TX5). The protein is shown with a white cartoon/stick representation, and the 2mFO − DFC NSL density map is shown with a blue mesh (contoured at 2.5 σ). (E) An extensive hydrogen bond network connects the Asn37 side chain with a surface histidine (His86). The P43 structure (protomer A, PDB code 7TX3) and the corresponding 2mFO − DFC NSL density map are shown with a blue mesh (contoured at 2.5 σ). (F) An aromatic-thiol bond was observed between Tyr68 and Cys81 in protomer A of the P43 structure (PDB code 7TX3). The 2mFO − DFC NSL density map is shown with a blue mesh (contoured at 1 σ).