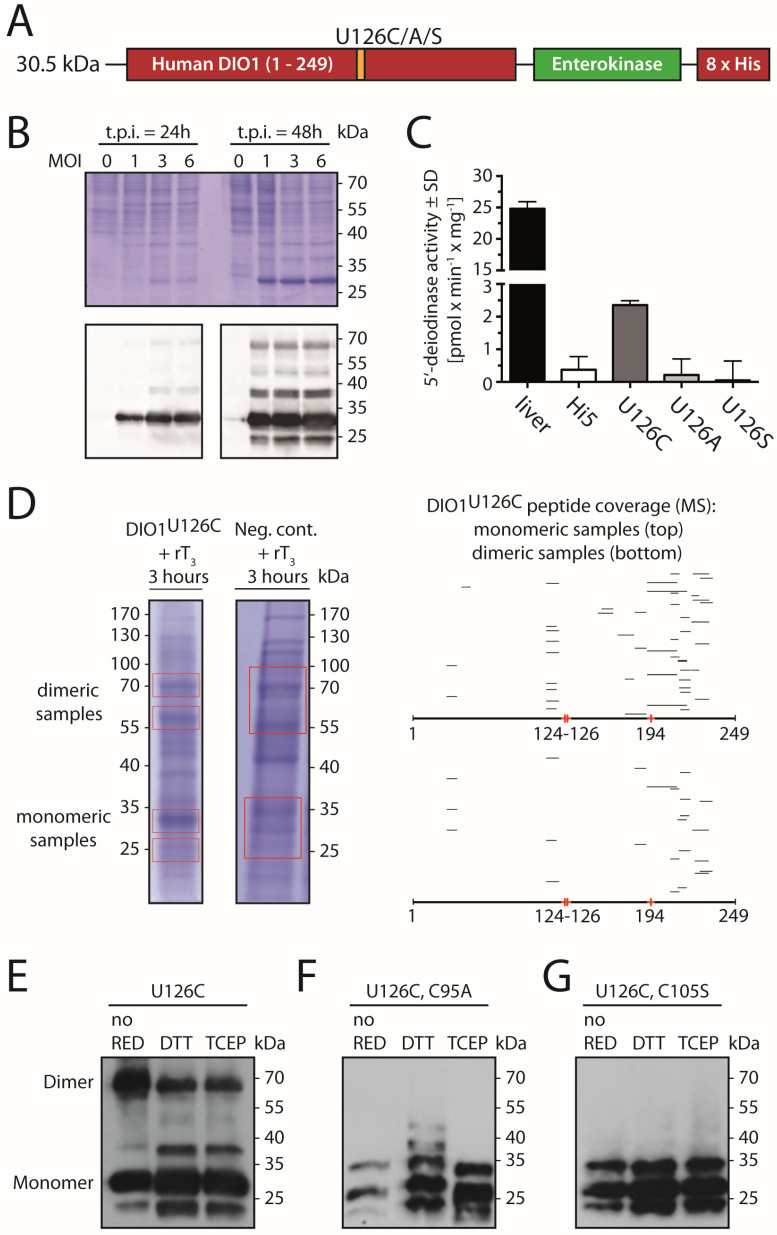
Figure 2.
Biochemical characterization of recombinant human DIO1U126C expressed in insect cells. (A). Construct. A C-terminal His-tag was added to the human DIO1 sequence separated by an enterokinase cleavage site. (B). Electrophoretic mobility of DIO1U126C expressed in Hi5 cells 24 h and 48 h post-infection (t.p.i.) with baculovirus. MOI, multiplicity of infection. Upper panel Coomassie-stained gel, lower panel immunodetection with anti-His-tag antibody. (C). Catalytic activity of recombinant DIO1U126C compared to negative controls (DIO1U126A, DIO1U126S, and non-infected Hi5 cells). Mouse liver homogenate served as positive control. SD standard deviation. (D). Detection of DIO1U126C-derived peptides by mass spectrometry. Regions encompassing “monomeric” and “dimeric” bands were cut from Coomassie-stained gels loaded with protein from DIO1U126C-expressing cells and non-infected controls after incubation with rT3 for 3 h. Right panel, peptide coverage of DIO1 found in tryptic digests of gel slices. (E–G). Western blotting against His-tag following non-reducing SDS-PAGE of recombinant DIO1 pretreated with or without reductants (DTT or TCEP).