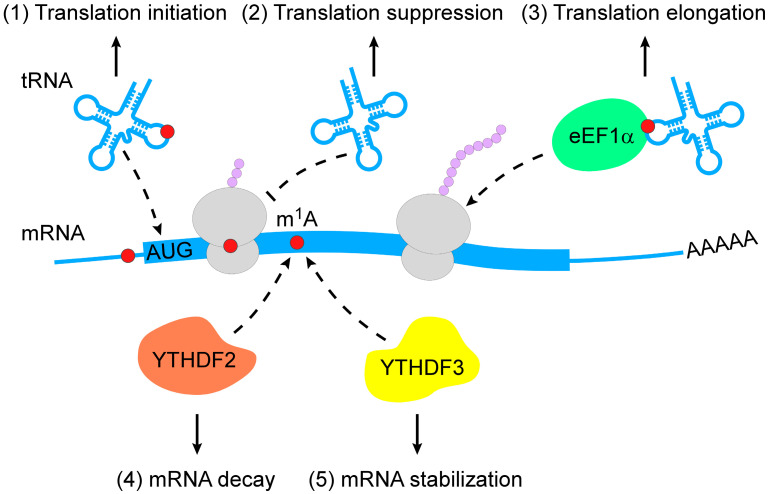
Figure 2.
Action mechanisms of m1A in RNA metabolism. m1A RNA modification regulates RNA metabolism in multiple layers (from top to bottom: (1) m1A RNA modification stabilizes tRNAs to promote translation initiation; (2) m1A-modified mRNAs interfere with Watson–Crick base-pairing with tRNA to suppress translation; (3) m1A-modified tRNAs are coupled with eEF1α to polysomes to promote translation elongation; (4) m1A-modified mRNAs are subjected to degradation by interacting with YTHDF2; (5) m1A-modified mRNAs become stable when they bind to YTHDF3). m1A, N1-methyladenosine; eEF1α, eukaryotic elongation factor 1-α; YTHDF, YTH domain-containing family protein.