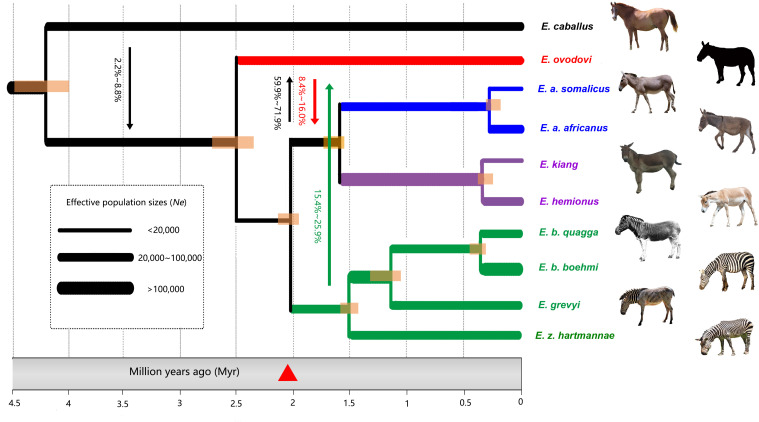
Figure 3. Demographic model for extinct and extant equine lineages as inferred by G-PhoCS (Gronau et al., 2011).
Node bars represent 95% confidence intervals. The width of each branch is scaled with respect to effective population sizes (Ne). Independent Ne values were estimated for each individual branch of the tree, assuming constant effective sizes through time. Migration bands and probabilities of migration (transformed from total migration rates) are indicated with solid arrows. The red triangle indicates the earliest Sussemionus evidence found in the fossil record. (Images: E. caballus by Infomastern, E. a. somalicus by cuatrok77, E. kiang by Dunnock_D, E. a. africanus by Jay Galvin, E. hemionus by Cloudtail the Snow Leopard, E. z. hartmannae by calestyo, E. b. quagga by Internet Archive Book Images, E. b. boehmi by GRIDArendal, and E. grevyi by 5of7.)