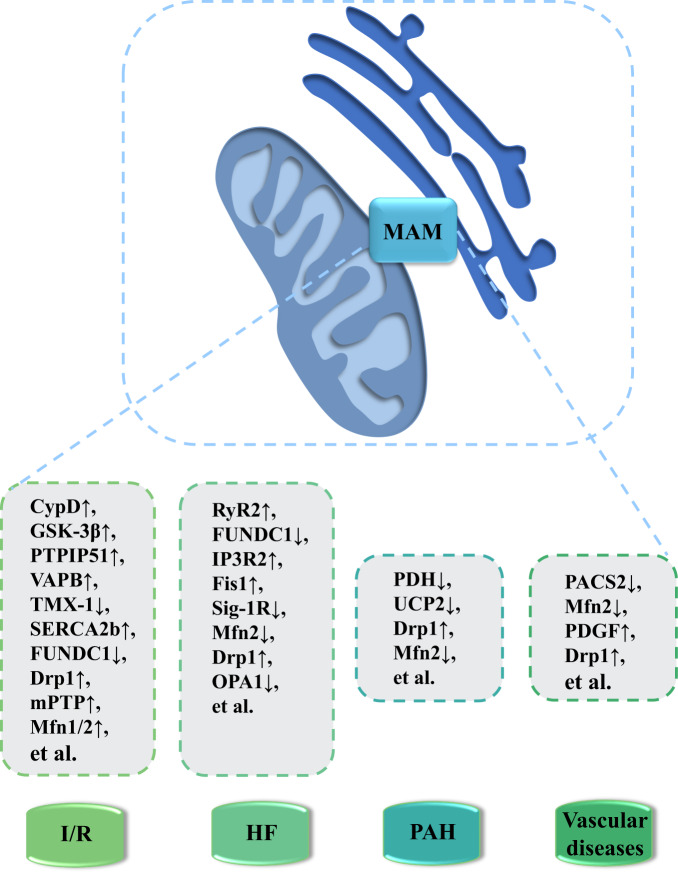
Fig. 3. MAM-enriched proteins as potential new therapeutic targets for the treatment of CVD pathologies.
Disruption or deficiency in ER-mitochondria communication is crucial in the pathogenesis of various CVDs such as I/R, HF, PAH and vascular diseases. For example, expression level of CypD, PTPIP51 and mPTP is elevated in I/R, whereas downregulation of FUNDC1, Sig-1R and OPA1 is noted in HF. Drp1 level is increased while Mfn2 level is decreased in PAH and vascular diseases. Notably, the key regulatory proteins of these processes serve as promising therapeutic targets in the management of these pathological conditions. Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular diseases; CypD, Cyclophilin D; Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; Fis1: fission protein 1 homolog; FUNDC1, FUN14 domain containing 1; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; HF, heart failure; IP3R2, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors 2; I/R, ischemia-reperfusion; MAM, mitochondria-associated membrane; Mfn1/2, mitofusin-1 and -2; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pores; OPA1, optic atrophy 1; PACS2, phosphofurin acidic cluster sorting protein 2; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PTPIP51, protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51; RyR2, ryanodine receptor 2; SERCA2b, sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2 + -ATPases 2b; Sig-1R, sigma-1 receptor; TMX-1, thioredoxin 1; UCP2, uncoupling protein 2; VAPB, vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein-B.