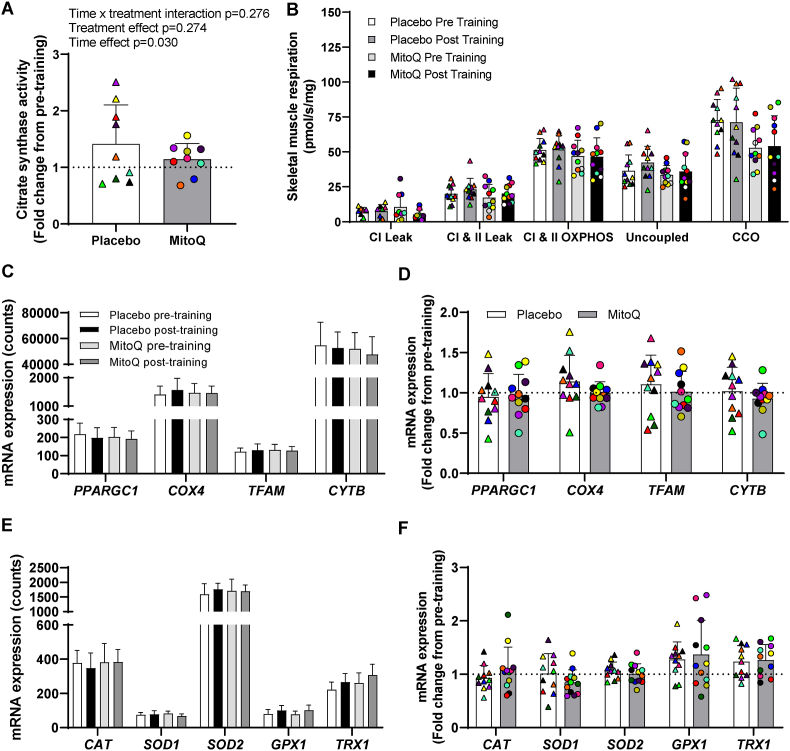
Fig. 5.
The effect of MitoQ supplementation on markers of mitochondrial content and function and antioxidant enzyme expression in skeletal muscle following HIIT. A) Skeletal muscle citrate synthase activity following 3 weeks of HIIT presented as fold change from pre-exercise. B) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration before and after 3 weeks of HIIT. C) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial gene expression before and after 3 weeks of HIIT. D) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial gene expression following 3 weeks of HIIT presented as fold change from pre-exercise. E) Skeletal muscle antioxidant gene expression before and after 3 weeks of training. F) Skeletal muscle antioxidant gene expression following 3 weeks of training presented as fold change from pre-exercise Triangles and circles represent individual values. The effect of training and MitoQ supplementation on markers of skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis was measured using two-way repeated measures ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± SD. PPARGC1A; Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-Alpha, COX4; Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4, TFAM; Mitochondrial Transcription Factor A, CYTB; Cytochrome B, CAT; Catalase, TRX1; Thioredoxin 1; GPX1; Glutathione peroxidase 1, SOD1; Superoxide Dismutase 1, SOD2; Superoxide Dismutase 2.