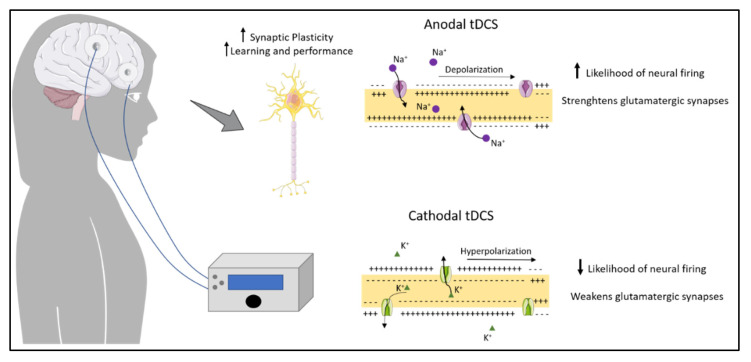
Figure 2.
Effects of anodal and cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). The figure represents cortical neurostimulation that could increase synaptic plasticity, leading to improvements in learning and memory. Anodal stimulation increases the likelihood of neuronal firing, strengthening glutamatergic synapses and increasing excitation. Cathodal stimulation decreases likelihood of neuronal firing, weakening glutamatergic synapses and decreasing excitation.