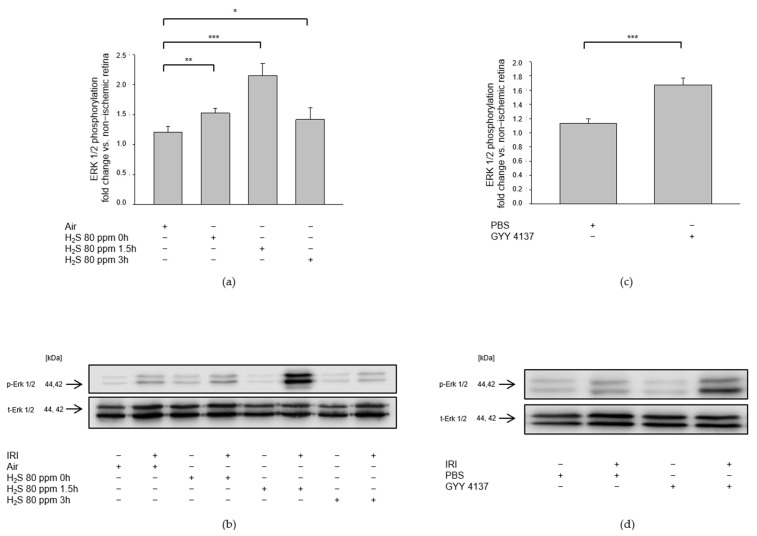
Figure 3.
Effect of H2S on retinal ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) 1/2 phosphorylation after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Rats were treated either with inhalation of 80 ppm H2S for 60 min at various time points after IRI or with the intravenous application of the slow-releasing H2S donor GYY 4137 immediately following IRI. Retinal homogenates were used for Western blot analysis. (a,c) Densitometric analysis of ERK1/2 phosphorylation after inhalation of 80 ppm H2S at 0, 1.5, and 3 h after IRI (data are mean ± SD, n = 8, ** = p < 0.01, IRI vs. IRI + 80 ppm H2S at 0 h, *** = p < 0.001, IRI vs. IRI + 80 ppm H2S at 1.5 h, and * = p < 0.05, IRI vs. IRI + 80 ppm H2S at 3 h after IRI) and after IRI and treatment with GYY 4137 (data are mean ± SD, n = 6, *** = p < 0.001, IRI vs. IRI + GYY 4137). (b,d) Representative Western blot images showing the enhancement of ERK 1/2 phosphorylation after IRI and H2S inhalation (n = 8) and after IRI and treatment with GYY 4137 (n = 6).