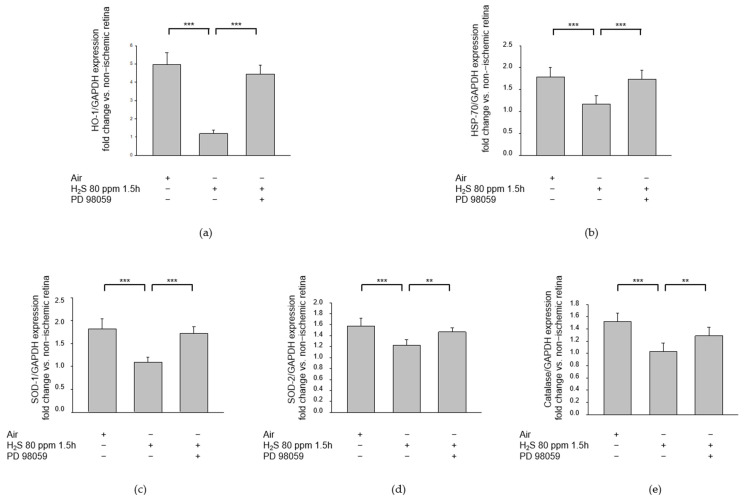
Figure 11.
Effect of H2S and the ERK (extracellular signal-regulated) pathway inhibitor PD 98059 on retinal heat shock response after ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Rats were subjected to unilateral retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and subsequently received inhalative therapy with 80 ppm H2S at 1.5 h after IRI, with or without the intravenous administration of ERK pathway inhibitor PD 98059. Retinal homogenates were used for analysis by quantitative real-time PCR. All results were normalized to GAPDH. (a–e) Fold induction of (a) HO-1 (heme oxygenase 1) mRNA expression, (b) HSP-70 (heat shock protein 70) mRNA expression, (c) SOD-1 (superoxide dismutase 1) mRNA expression, (d) SOD-2 (superoxide dismutase 2) mRNA expression, and (e) catalase mRNA expression after IRI. An 80 ppm H2S inhalation at 1.5 h after IRI was able to attenuate this increase in heat shock response. This effect was counteracted by the ERK pathway inhibitor PD 98059. (Data are mean ± SD, n = 8 for IRI and IRI + 80 ppm H2S, n = 6 for IRI + 80 ppm H2S + PD 98059, *** = p < 0.001, IRI vs. IRI + H2S, IRI + H2S vs. IRI + H2S + PD 98059 for HO-1, HSP-70, and SOD 1, ** = p < 0.01, IRI + H2S vs. IRI + H2S + PD 98059 for SOD-2 and Catalase).