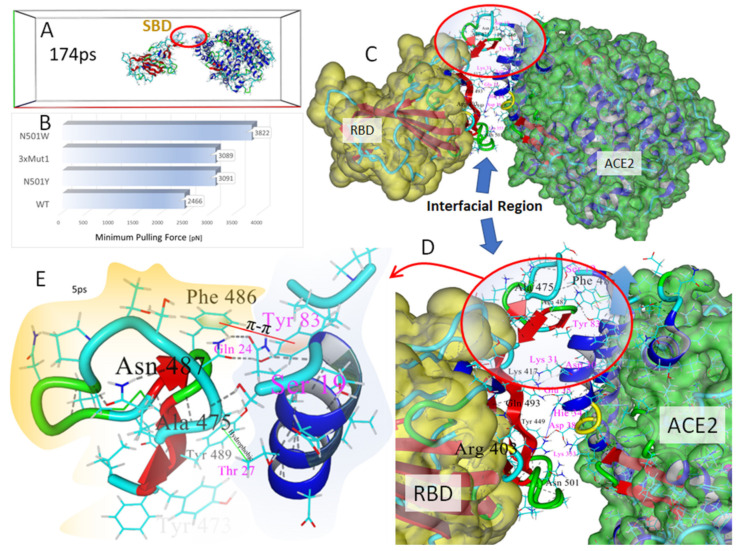
Figure 9.
Interactions in the “strong binding domain” (SBD) of the wild-type RBD-ACE2 complex (6LZG). The SBD at the “top” of the interfacial region (circled in red) approximately comprised RBD residues 474–490 and ACE2 residues 19–22 and 78–83. The ACE2 SBD region is dominated by the two parallel alpha-helical regions that overlay the central zinc cavity of ACE2. (A) View of RBD-ACE2 complex at 174ps of SMD simulation time following near complete dissociation of the proteins. Note that the “strong binding domain” (SBD) was the last region to undergo dissociation. (B) Minimum pulling force (MPF) required for complete dissociation of the RBD-ACE2 complexes as a function of mutant type. (C) Wild-type RBD-ACE complex showing overview of interfacial zone after initial system equilibration and 104ps of SMD. RBD residue labels are shown as black; ACE2 labels as magenta. (D) Magnified view of interfacial region indicating significant intermolecular interactions, including: strong salt bridge from Arg402 of the RBD to Hie34 of ACE2 (blue line in (D)); weak salt bridge from Lys417 of the RBD to Asp30 (gray-blue line in (D)); π-π interaction between Phe486 of the RBD with Tyr83 of ACE2; hydrogen bond between the N-terminus Ser19 of ACE2 and Ala475 carbonyl oxygen of the RBD (dotted lines); hydrogen bond between RBD Tyr 449 -OH group and ACE2 Asp38; and hydrogen bond between the RBD Gln493 and ACE2 Glu35. (E) Detail view of some of the principle attractive interactions in the SBD. These include numerous stabilizing hydrogen bonds (dotted lines), as well as a strong π-π interaction between Phe486 of the RBD and Tyr83 of ACE2. Asn487 of the RBD was involved in two hydrogen bonds to the -OH group of Tyr83 of ACE2 and the terminal carbonyl group of Gln 24 of ACE2. A hydrophobic interaction exists between RBD Tyr489 and ACE2 Thr27. The hydrogen bond between Ala475 of the RBD and Ser19 of ACE2 helped stabilize SBD interactions and was often the last bond to undergo dissociation as the proteins were pulled apart.