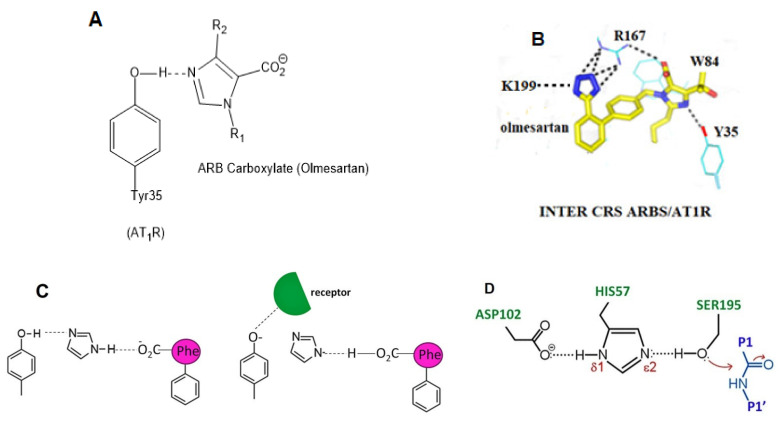
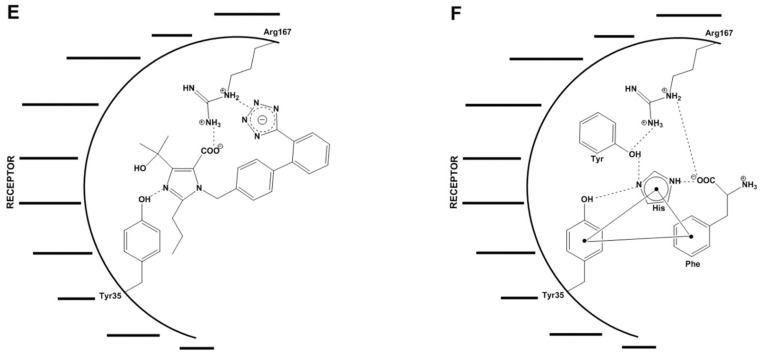
Figure 10.
Intermolecular interactions between AT1R and the ARB, Olmesartan. (A) Explanatory graph depicting the hydrogen bond interaction between AT1R Tyr35 hydroxyl with Olmesartan imidazole nitrogen. (B) Interactions of AT1R residues K199, R167, W84, Y35 with olmesartan from crystal protein bank [45,46]. Note. ARBs may be inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 binding through strong interactions between negatively charged tetrazolate and carboxylate with polybasic arginines cavity loop 681–686 S protein RBD of SARS-CoV-2. (C) Tyrosine (Tyr), histidine (His), and phenylalanine (Phe) aromatic side chains and c-terminal carboxylate are intra connected to create a cyclic compact structure that triggers activity through Tyr hydroxylate. (D) His and asparagine (Asp) carboxylate in serine proteases are intra connected to create the CRS in serine proteases. (E) Explanatory graph depicting inter molecular interactions between EXP3174 negative groups histidine carboxylate and biphenyl tetrazolate with positively charged AT1R residue arginine 167. Tyr35 hydroxylate of AT1R interacts with biphenyl imidazole nitrogen. (F) Explanatory graph depicting intra molecular interactions between AngII with AT1R167 and Tyr35. Note: The interactions between AT1R Arg167 with His carboxylate and biphenyl tetrazolate can occur in silico between SARS-CoV-2 basic loop Args with carboxylate and tetrazolate of ARBs.