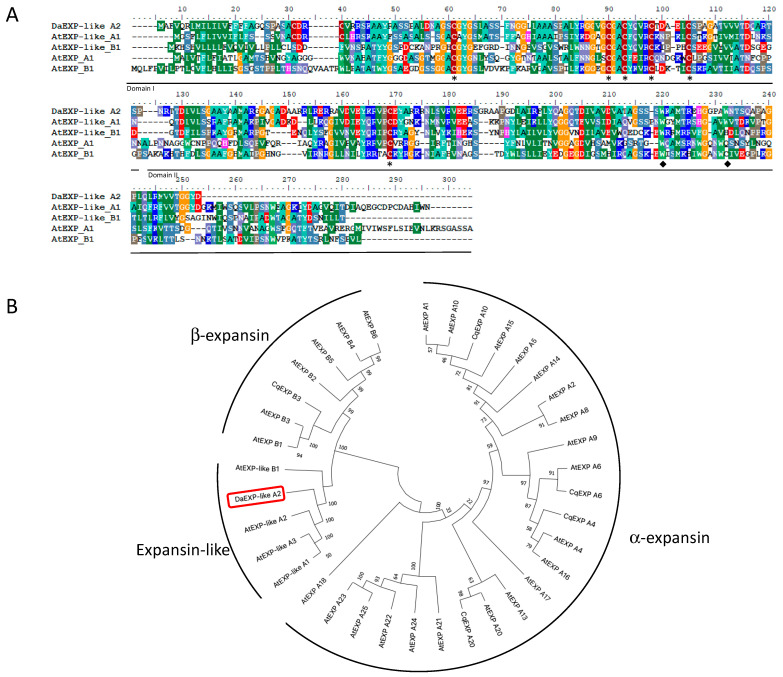
Figure 4.
DaEXLA2 sequence analysis. (A) Multiple sequence alignment between different expansin proteins. Letters with the same color are identical residues or similar residues. Meanwhile, gaps are indicated by dashes. Asterisks show conserved Cys residues (C) of expansin proteins. Black diamonds indicate aromatic tryptophan residues (W) of expansins proteins. (B) Phylogenic analysis of the expansin from D. antarctica with the following different plant orthologs proteins: Arabidopsis thaliana AtEXPA1 (AEE34945), AtEXPA2 (AED90852), AtEXPA4 (AEC09708), AtEXPA5 (AEE77523), AtEXPA6 (AEC08194), AtEXPA8 (AEC09854), AtEXPA9 (AED90451), AtEXPA10 (AEE30732), AtEXPA13 (AEE73914), AtEXPA14 (AED96748), AtEXPA15 (AEC05663), AtEXPA16 (AEE79393), AtEXPA17 (AEE82054), AtEXPA18 (Q9LQ07), AtEXPA20 (NP_195534), AtEXPA21 (AED94413), AtEXPA22 (AED94414), AtEXPA23 (AED94415), AtEXPA24 (NP_198747), AtEXPA25 (AED94417), AtEXPB1 (AEC07066), AtEXPB2 (NP_564860), AtEXPB3 (AEE85459), AtEXPB4 (NP_182036), AtEXPB5 (NP_191616), AtEXPB6 (AEE34411), AtEXLA1 (AEE78096), AtEXLA2 (AEE86923), AtEXLA3 (AEE78095), AtEXLB1 (O23547). Colobanthus quitensis CqEXPA4 (MZ190884), CqEXPA6 (MZ190885), CqEXPA10 (MZ190886), CqEXPA20 (MZ190887), and CqEXPB3 (MZ190888).