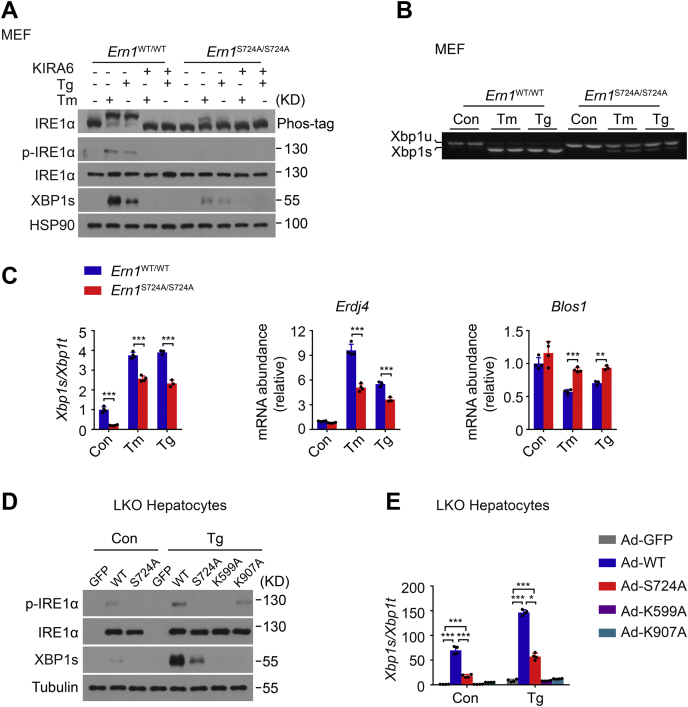
Figure 2.
S724A mutation results in lower IRE1α autophosphorylation with reduced RNase activity upon ER stress.A, MEF cells derived from Ern1WT/WT and Ern1S724A/S724A mice were treated with DMSO (−), 10 μg/ml Tm, for 4 h or 1 μM Tg for 2 h after preincubation for 30 min with DMSO (−) or 10 μM KIRA6, the IRE1α kinase inhibitor. Immunoblot analysis of IRE1α autophosphorylation by Phos-tag gel and its phosphorylation at Ser724 using anti–phospho-IRE1α antibody. HSP90 was used as the loading control. B and C, MEF cells of the indicated genotypes were likewise treated with DMSO (Con), Tm, or Tg. B, agarose gel analysis of Xbp1 mRNA splicing by RT–PCR. Shown are PCR products corresponding to the unspliced Xbp1u and spliced Xbp1s mRNA. C, quantitative RT–PCR analysis of Xbp1 mRNA splicing, shown as the ratio of spliced (Xbp1s) to total (Xbp1t) Xbp1 mRNA, along with the abundance of Erdj4 and Blos1 mRNA. D and E, primary hepatocytes from male liver–specific IRE1α knockout (LKO) mice were infected for 48 h with adenoviruses expressing GFP, WT, or the indicated mutant human IRE1α proteins and subsequently treated for 2 h with DMSO (Con) or 1 μM Tg. D, immunoblot analysis of IRE1α protein and its phosphorylation at Ser724, along with the production of XBP1s protein. Tubulin was used as the loading control. E, quantitative RT–PCR analysis of Xbp1 mRNA splicing. All data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 2 or 3 independent experiments). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by two-tailed unpaired Student's t test. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HSP90, heat shock protein 90; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; RNase, ribonuclease; Tg, thapsigargin; Tm, tunicamycin; Xbp1, X-box binding protein 1.