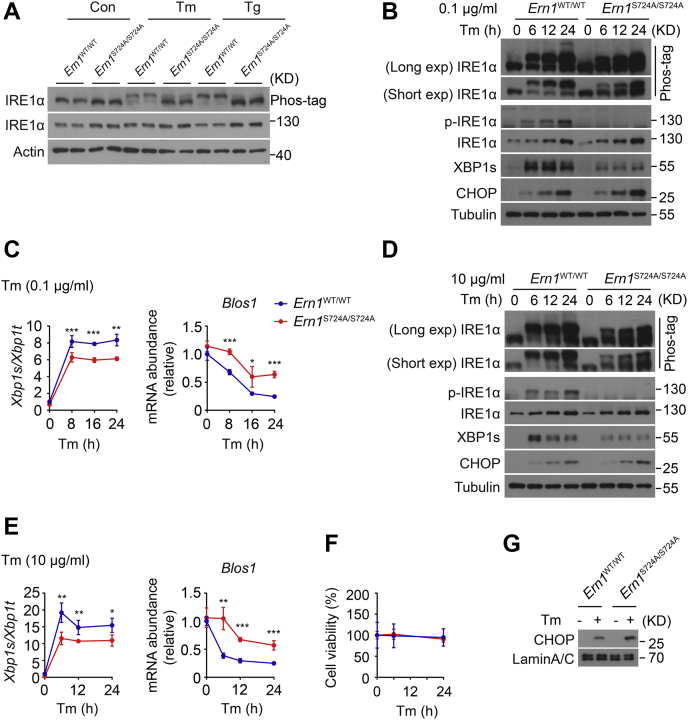
Figure 5.
Disruption of Ser724phosphorylation attenuates the RNase activation of IRE1α in hepatocytes.A, primary hepatocytes from mice of the indicated genotypes were treated with DMSO control (Con), 10 μg/ml Tm for 4 h, or 1 μM Tg for 2 h. Immunoblot analysis of IRE1α protein, with upper Phos-tag gel analysis of IRE1α phosphorylation. Actin was used as the loading control. B–E, hepatocytes of the indicated genotypes were treated with 100 ng/ml or 10 μg/ml Tm for the indicated time intervals. B and D, immunoblot analysis of IRE1α phosphorylation along with XBP1s and CHOP protein levels. Upper Phos-tag gels are shown for the band-shift analysis of IRE1α protein phosphorylation with long or short exposure time. Tubulin was used as the loading control. C and E, quantitative RT–PCR analysis of Xbp1 mRNA splicing and the RIDD target Blos1 mRNA. F and G, hepatocytes were treated with 10 μg/ml Tm. F, cell viability analysis by CCK8 assay. G, immunoblot analysis of nuclear CHOP protein after 24 h of 10 μg/ml Tm treatment. Lamin A/C was used as the nuclear protein control. All data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 2 or 3 independent experiments). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test or two-way ANOVA. CCK8, Cell Counting Kit-8; CHOP, CCAAT-enhancer binding protein homologous protein; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α; RIDD, regulated IRE1-dependent decay; RNase, ribonuclease; Tg, thapsigargin; Tm, tunicamycin; XBP1s, spliced X-box binding protein 1.