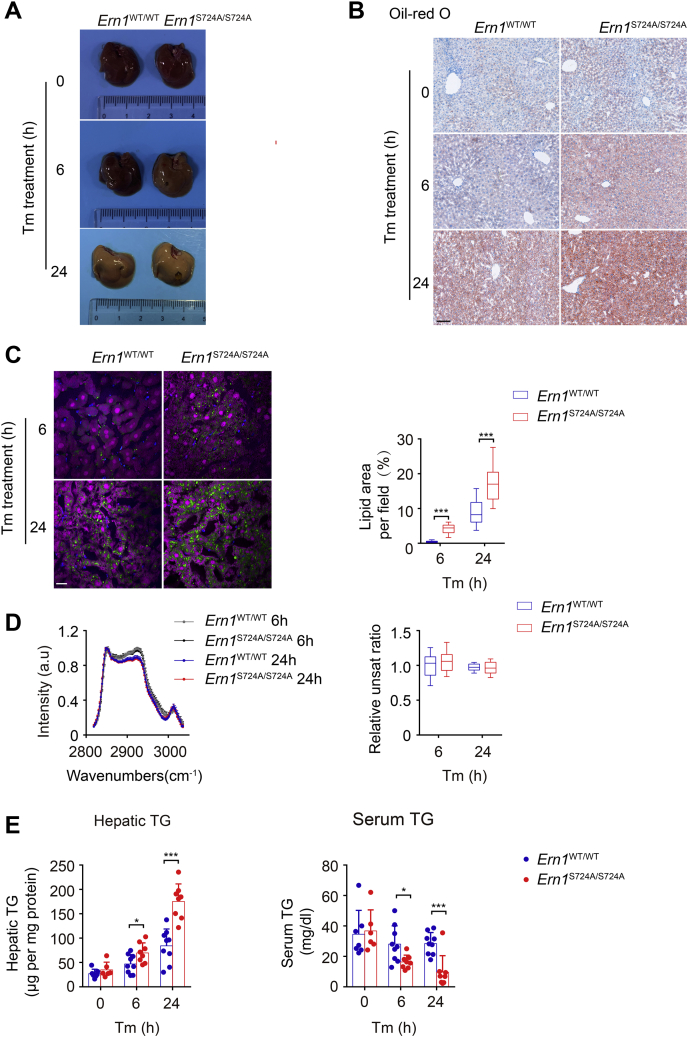
Figure 6.
S724A mutation of IRE1α results in aggravated hepatic steatosis with reduced plasma lipids under ER stress. Male Ern1S724A/S724A mice and their Ern1WT/WT littermates at 2 months of age were injected i.p. with Tm (1 mg/kg body weight) and sacrificed at 6 or 24 h after Tm treatment (n = 6–9 per group). Mice treated with 150 μM dextrose was used as the vehicle control group. A, representative liver images. B, representative images of Oil-Red O staining of livers (n = 3 per group). The scale bar represents 100 μm. C, representative hsSRS images of liver sections from mice at 6 and 24 h after Tm injection. Imaging analysis by the Multivariate Curve Resolution (MCR) algorithm showing chemical distributions of lipid (green), lipofuscin (blue), and protein (magenta) in a field of 200 × 200 μm2 (300 × 300 pixels with dwell time of 10 μs/pixel for imaging). Lipid contents were quantified as areas of lipid signals per field using ImageJ (n = 3 per group). The scale bar represents 20 μm. D, the average hsSRS spectra of hepatic lipids. The Raman peak at 3007 cm−1 represents the vibration from unsaturated =CH stretch. The degree of lipid unsaturation was evaluated by the ratio of Raman intensity at 3007 and 2853 cm−1. E, liver and serum levels of triglycerides. Data represent the mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; hsSRS, hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme 1α; Tm, tunicamycin.