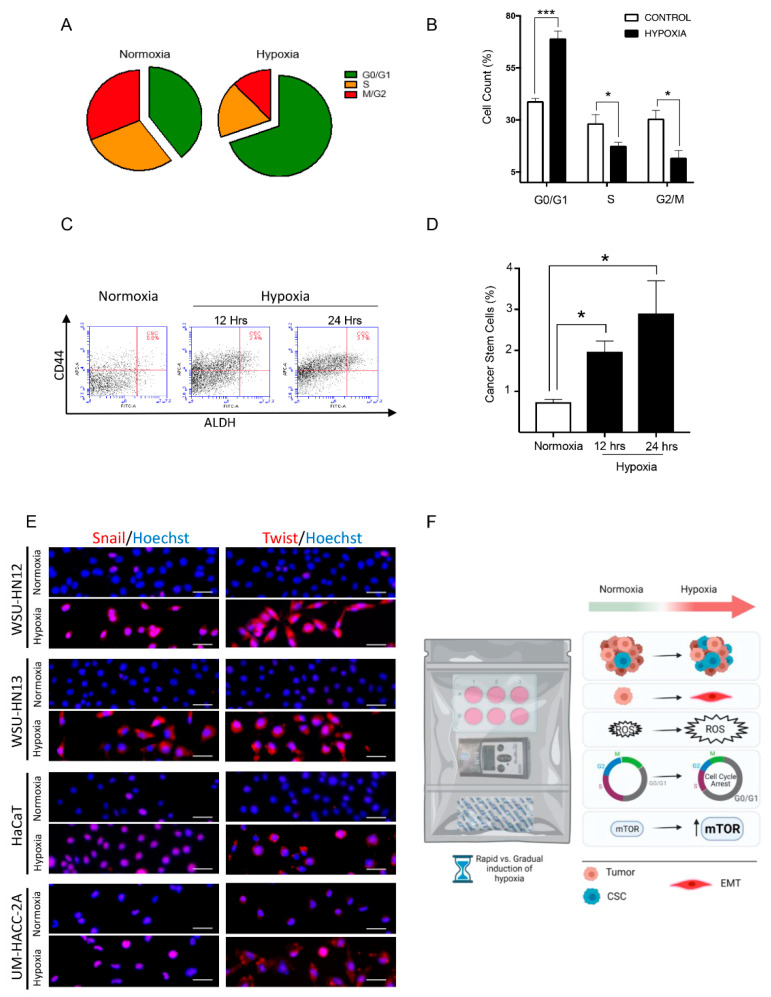
Figure 4.
Deoxidizing absorbers method induces cell cycle arrest, accumulation of cancer stem cells, and accumulation of Snail and Twist. (A,B) The pie graphic demonstrates an increased number of cells in the G0/G1 phase under hypoxia compared to normoxia (*** p < 0.001). (C,D) Deoxidizing absorbers induced the continuous accumulation of cancer stem cells measured at baseline (normoxia), 12 h, and 24 h (ALDH+/CD44++ positive cells) (* p < 0.05). (E) Immunofluorescence staining for Snail and Twist on 4 different epithelial cell lines. WSU-HN12 and WSU-HN13 are squamous cell carcinomas, HaCaT is a human immortalized skin cell line, and UM-HACC-2A is a salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma cell line. Note the weak immunofluorescence staining for Snail (Alexa 568—red) in all 4 cell lines cultured under normoxia compared with hypoxic conditions (scale bar 50 µm). Immunofluorescence staining for Twist (Alexa 568—red). Note the weak staining in all 4 cell lines cultured under normoxia and accumulation of Twist in all cell lines during hypoxia. Hoechst 33,342 counterstaining for DNA content is in blue (scale bar 50 µm). (F) Diagram representing the biological effects of deoxidizing-absorbers-induced hypoxia over epithelial cells. Deoxidizing absorbers may be used to achieve rapid vs. gradual onset of hypoxia. They are also effective in triggering the EMT phenotype in epithelial cells, increasing the intracellular levels of ROS, activating the mTOR pathway, inducing cell cycle arrest (G0/G1), and in promoting the accumulation of cancer stem cells.