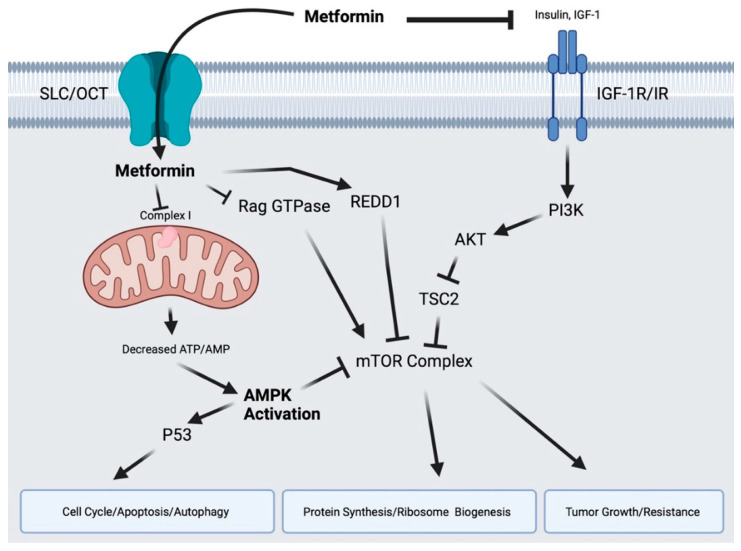
Figure 2.
Molecular effects of metformin in cancer cells. Metformin directly inhibits complex I of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria resulting in decreased ATP/AMP ratio and activation of AMPK. AMPK activation inhibits mTOR and activates P53 to impact subsequent cellular processes. Metformin also inhibits mTOR in an AMPK-independent manner, through Rag GTPases and REDD1. Reduced insulin availability through metformin’s systemic effects indirectly modulates the proliferative pathway, PI3K/AKT. AMP: Adenosine Monophosphate; AMPK: AMP-Activated Protein Kinase; ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate; IGF: Insulin-like Growth Factors; IGF-R: Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor; mTOR: Mammalian Target of Rapamycin; OTC: Organic Cation Transporter; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; REDD1: Regulated in Development and DNA damage responses 1; SLC: Solute Carrier Transporter; TSC2: Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2. Created in BioRender.