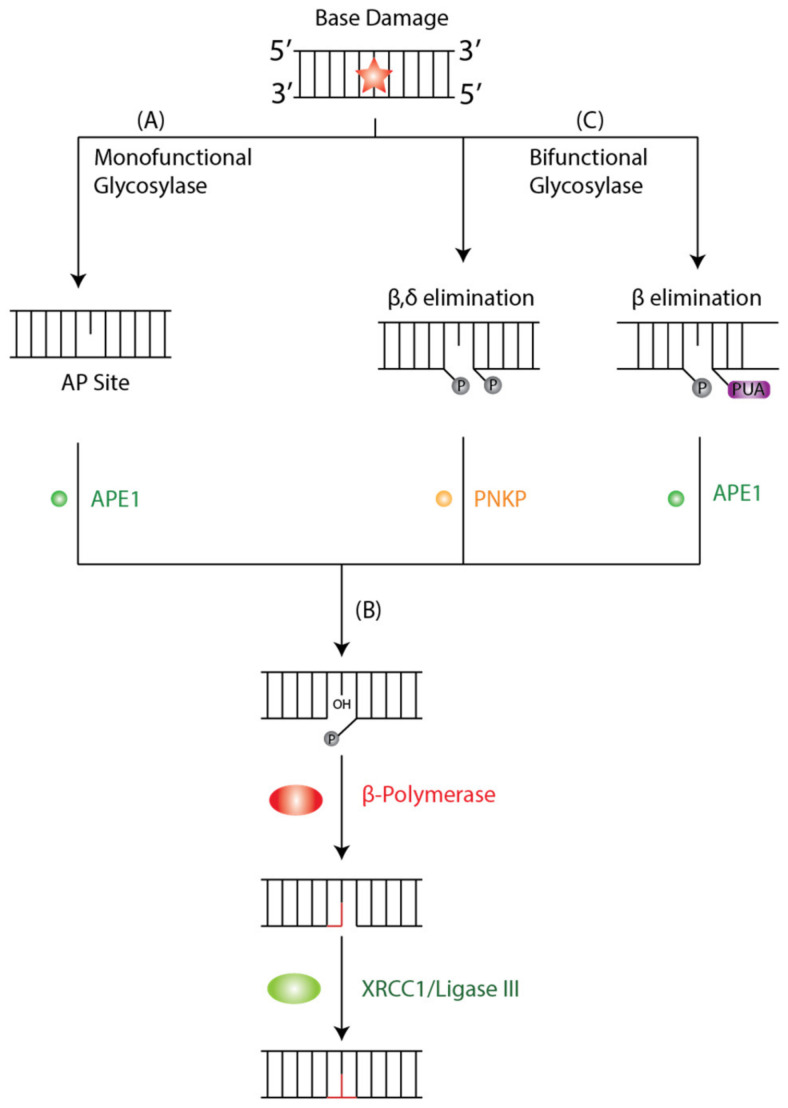
Figure 1.
Schematic Representation of BER Pathway. BER is initiated by DNA Glycosylases that recognize and bind to a base lesion. (A) Monofunctional Glycosylases will identify the DNA lesion and catalyze the hydrolysis of the N-glycosyl bond that releases the damaged base and generates an AP site that is processed by APE1. (B) A bifunctional glycosylase will recognize and remove oxidative lesions either through β,δ or β-elimination to create a single strand break. The 3′ α,β-unsaturated aldehyde and 5′ phosphate are further processed by PNKP and APE1, respectively. (C) Subsequently, Polβ and XRCC1/Ligase III fill and seal the single nucleotide gap and restore the original base sequence. The orange star denotes base damage.